Measures taken in hospital management following the impact of the coronavirus pandemic.
European Statement
Selection, Procurement and Distribution
Why was it done?
The aim of the study is to assess the crisis impact on the consumption of pharmaceutical products in the intensive care unit in order to estimate, rationalize the need and prevent supply problems.
What was done?
Due to Covid-19 pandemic and its major economic impact, we carried out a comparative study of the consumption of pharmaceutical products in the intensive care unit before and during the crisis.
How was it done?
A list of pharmaceutical products to be evaluated has been established beforehand. The choice was made for the products most used in intensive care units in accordance with the recommendations of COVID management. The list includes drugs and medical devices.
In order to compare the consumption of these products in terms of quantity and cost, data collection was carried out over two periods, each of 6 months, before and during the crisis in Tunisia. The first from January 1st, 2019 to June 30th, 2019, the second from January 1st, 2021 to June 30th, 2021.
What has been achieved?
As a result of this assessment, it was possible to quantify the increase in several drugs and medical devices. It led us to:
-modulate our supply of these products
-take rationalization measures in cooperation with doctors
-develop management protocols according to the recommendations and available products
– close monitoring of prescriptions and compliance with protocols in order to optimize consumption, avoid any abuse and limit breaks as much as possible.
Tab. Variation of consumption and cost
Product Consumption2019 Consumption2021 Variation factor of the consumption Variation factor of the cost
Hypnotic curares 25 170 6.8 8.1
Antithrombotics 647 2286 3.5 8.1
Antibiotics 932 4060 4.4 11.2
Fluconazole 240 378 1.6 1.9
Dexamethasone 845 1268 1.5 2.0
Isolation gown 740 6925 9.4 7.8
Masks 6100 13300 2.2 2.2
hydroalcoholic products 123 217 1.8 1.8
What next?
A generalization of the drafting and updating of the protocols concerning the management and the dispensing is programmed for all the other departments which will be validated by the therapeutic committee and the antibiotics committee.
OPTIMIZATION AND CENTRALIZATION OF THE HANDLING CIRCUIT OF HAZARD DRUGS FROM THE PHARMACY SERVICE
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Mireia Iglesias Rodrigo, Júlia Pardo Pastor, Alba Manzaneque Gordon, Cristina Sangrador Pelluz, Núria Meca Casasnovas, Clara Sebastián Carrasco, Fernando Salazar Gonzalez, Gemma Garreta Fontelles, Jordi Nicolás Picó
Why was it done?
Due to the risk posed by the handling of Hazard Drugs (HD) in the healthcare field, it is necessary to implement circuits that guarantee the professional’s safety.
What was done?
Create an internal classification of HD based on the NIOSH List of Hazard Drugs in Healthcare Setting 2020, to optimize the circuit of its handling from its receiving to its administration.
How was it done?
Considering the HD included in the Pharmacotherapeutic Guide (PTG) of our center, the stages of reception and adaptation/preparation/dispensing/administration and other precautions were analyzed.
Categories were established, analyzing the needs of each stage according to: NIOSH level of danger, setting (inpatient/outpatient), pharmaceutical form, commercialized pharmaceutical specialties or available alternatives, and material/personal resources.
Prior to its implementation, e-learning training was carried out for the healthcare professional involved.
What has been achieved?
A total of 25.3% (379/1498) of the pharmaceutical specialties included in PTG were HD. Thirteen HD groups were identified. Due to the fact that in the outpatient setting the drug is dispensed to the patient in its original container, the actions implemented were only carried out for inpatients, representing these 9/13 of described groups. The established training was carried out by the 89% of professionals. Proposed measures for HD are summarized in Table 1.
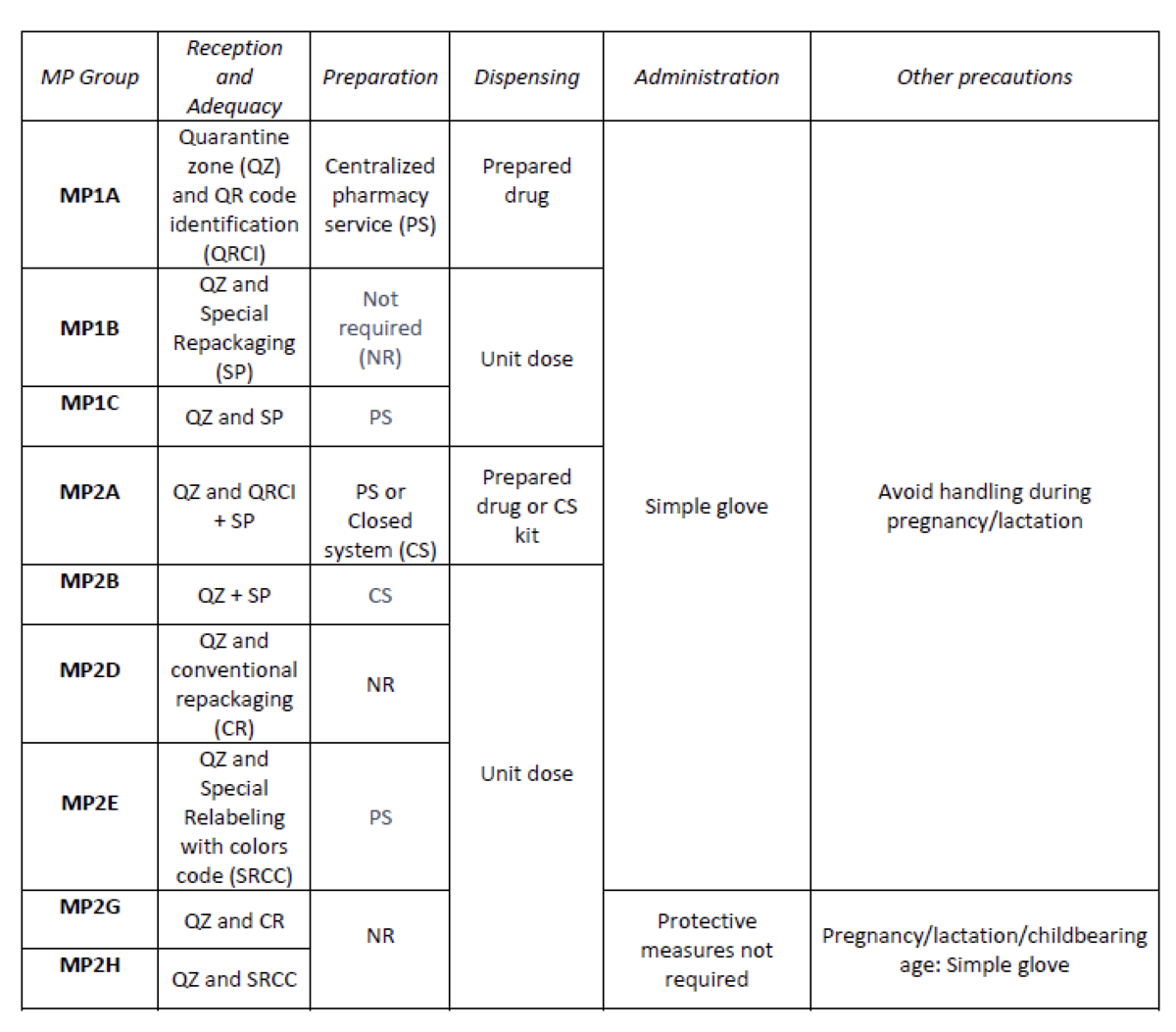
What next?
Monitoring and evaluation of the circuit
Case-study: Pharmaceutical teleconsultation using a mobile application
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Joana Russo, Maria João Ribeiro, Humberto Gonçalves, Joana Ribeiro, Silva Cristina, António Gouveia
Why was it done?
In our country the oncology medication for ambulatory patients is dispensed by the hospital pharmacist (HP). Due to several aspects (i.e., COVID-19 pandemic) the process of distribution of said medication has changed in that the HP and the patient no longer meet face to face (Drive-thru systems, proximity projects in which the medication is sent to a nearby pharmacy of the patients living area). A tool was required that enabled the HPs to continue to monitor the relevant clinical aspects (patient education; medication adherence (MA), drug interactions (DI) and adverse events (AE) evaluation).
What was done?
We used a mobile application (App) to conduct the pharmaceutical evaluation of clinical aspects that need to be considered when dispensing oncology medication.
How was it done?
In collaboration with the Information Technologies department of our hospital, an App was developed. It integrates the patient’s hospital prescriptions and their answers to an adaptive query that identifies cases that need further clinical data We selected a specific drug (ibrutinib) and developed an algorithm that presented the extended questions accordingly. The App was announced to patients that required hospital medication and wanted to receive it through an alternative method of distribution.
What has been achieved?
In little over a year, a total of 1720 requests were received (668 patients). The algorithm was successful in differentiating patients whose evaluation needed to include additional clinical information. In 22 requests, further data was automatically gathered (9 patients) enabling us to evaluate MA, DI and AE. These teleconsultations do not require additional professionals (ie an assistant to register the request) nor a compatible time slot for a pharmacist-patient phone call.
What next?
The results showed that the concept of pharmaceutical teleconsultations through an App is viable and we intend to extend its range to other drugs and to dissociate the teleconsultation from the dispensing request. This approached also showed that proximity between HP and patients was positively affected allowing patients to consult their hospital pharmacist whenever they need to and wherever the patient was.
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN APPOINTMENT MANAGEMENT MODULE APPLIED TO THE OUTSIDE PATIENT AREA
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
JUDIT PERALES PASCUAL, ANA PÉREZ LÓPEZ, HERMINIA NAVARRO AZNAREZ, ELENA HERRANZ BAYO, MARIA PEREZ MORENO, CARLOS-IGNACIO DIAZ CALDERON HORCADA, Mª REYES ABAD SAZATORNIL
Why was it done?
In 2019 the UPEX attended a large volume of patients without a scheduled appointment, long waits were generated and the pharmacotherapeutic follow-up was complicated. The purpose was to implement an appointment management module to avoid crowds, excessive waiting times, allowing better organizational management of care and knowledge of patients in each type of consultation.
What was done?
An outpatient is a patient who goes to the outpatient unit of their Hospital Pharmacy Service to collect a drug for hospital use/diagnosis or foreign drug (it will be administered without health personnel intervention).
An appointment management system was implemented in accordance with the objectives of the SAMPA project (Service for Registration and Promotion of Adherence to Medicines for Elderly Patients), included in the European STOPandGo project.
How was it done?
Creating a cross-cutting system for the entire clinical circuit from prescription to dispensing involved a great deal computer involvement. Although it began to be used in November 2018, it was not used by the mostly part of prescribing doctors until the end of 2020.
Now, when the patient leaves medical consultation, he/she will go to the pharmacy and will be seen by a pharmacist. Besides, the program will propose a return appointment when it calculates that the patient has a week’s worth of medication, thus preventing the patient from running out of medication. The pharmacist will decide if the patient needs pharmacotherapeutic follow-up.
What has been achieved?
In 2019, 5 services cited patients while in 2020 it was 14; the percentage of patients attending pharmacy cited increased from 73.2%(2019) to 79.4%(2020).
Currently, the pharmacist knows in advance which scheduled patients he has and can establish a better organizational care management and determine in advance if the patient needs a close pharmacotherapeutic follow-up. Additionally, with this system an average waiting time of 03:55min was achieved (in 2019 appointments with waits >30min were recorded).
What next?
The implementation of the appointment management system has made possible to achieve better organizational management of care,avoid crowds,excessive waiting times, and provide better patient care and pharmacotherapeutic follow-up. The proposed solution can be extended to other hospitals.
TELEPHARMACY PROGRAMME IN CHRONIC NEUROLOGICAL PATIENTS DURING THE COVID PANDEMIC
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
ROSARIO MORA-SANTIAGO, JOSE-LUIS ORTIZ-LATORRE, ELENA SANCHEZ-YANEZ, ANGEL JURADO-ROMERO, ISABEL MOYA-CARMONA
Why was it done?
During the health alert caused by Covid-19, home delivery was quickly implemented in our country to reduce attendance at the Hospital Pharmacy Service (HPS) to obtain their medications.
In our HPS we transform home delivery into telepharmacy program (TP) with chronic neurological patients, who suffering pathologies that decrease their autonomy, with the purpose to optimize clinical outcomes and reduce the risk of contagion.
What was done?
The main purpose was to design a telepharmacy program (TP) undertstood as the provision of pharmaceutical care by pharmacists through the use of telecommunications to patients located at a distance. Telepharmacy services include patient follow-up and clinical service delivery. In our case, home delivery is also included.
How was it done?
We design the TP stratifying stable chronic patients (more than 6 months of treatment) by level of autonomy, physical distance to our Hospital and high risk (due to immunosuppressive treatment). Inclusion in the TP was proposed to patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) and aminotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Telepharmacy appointments were recorded and scheduled within the outpatient care activity, they were recorded in the patient’s medical history, as a pharmaceutical clinical follow-up, reviewing adherence, interactions and possible adverse events. Later, home delivery was made, through an external logistics company. Patients gave their consent to transfer personal data for home delivery.
Data collected were: sex and age, first or second line treatment in MS patients, pharmaceutical form (pill or syrup ) in ALS patients and number of total deliveries made.
What has been achieved?
We started on April 2020 with the program, six months later 56 patients were included, 48 with MS (total of MS patients attended by our HPS: 296) and 8 with ALS ( total of ALS patient attended by our HPS: 58). Median age: 45 years in MS group and 65 in ALS group. In MS group 37 patients received 1st line treatment and 10 second line. In ALS patients 6 received tablets and 2 syrup.
420 deliveries took place (average: 3,1 for patient).
What next?
The implementation of the TP was well accepted, avoiding longed displacement in patients with neurological pathologies. Our future target is to reach a greater number of patients that can be included in the program.
HOME DELIVERY SERVICE DURING COVID-19 PANDEMIC TO RHEUMATOLOGIC DISORDERS
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Ana Pelaez Bejarano, Maria de las Aguas Robustillo Cortes, Pilar Villar Santos, Olalla Montero Pérez, Ignacio Garcia Gimenez
Why was it done?
Rheumatologic disorders carry increased risk of infection compared with the general population, so facilitate access to hospital medications is of vital importance.
What was done?
On 14 March 2020, the Spanish government declared a state of alarm to deal with the spread of COVID-19. Medication dispensing protocols were immediately established to deliver drugs to patients who could not come in person to the hospital pharmacy department. These measures were designed to benefit citizens who, due to age or physical fragility, were more vulnerable to contagion. We had the collaboration of community pharmacies actively practicing during the COVID-19 pandemic and a logistics service, with no extra cost to the public healthcare system.
How was it done?
Between 30 March and 1 September 2020, a circuit was designed as follows: First, patient request the delivery service in the community pharmacy of their choice, which sending the request of each patient to college of pharmacists. Later, this institution sending of applications received from all pharmacies to hospital pharmacy. Here, the hospital pharmacist reviewed the patient’s electronic medical record, checking that the medication requested was appropriate, modifying it if deemed necessary (change of drug, dose, and so on). A pharmaceutical cooperative sending antirheumatic drugs to the community pharmacies. Finally, the community pharmacist who received the package checked the medication and, with the patient, reviewed and reinforced the information on the treatment.
What has been achieved?
587 patients were included: 211 rheumatoid arthritis, 173 psoriatic arthritis, 121 psoriasis and 82 ankylosing spondylitis. The delivery service enabled us to provide antirheumatic drugs to patients in their immediate environment through a service that was free for both the patient and the hospital pharmacy service. This contributes to guaranteeing the achievement of the pharmacotherapeutic objectives established for these patients.
What next?
Further action is needed to identify which groups of patients require more intensive pharmaceutical care and, therefore, who could benefit most from telepharmacy, and not only the delivery service.
IMPLANTATION OF A PHARMACEUTICAL CARE AND HOME DELIVERY CIRCUIT FOR OUTPATIENTS DURING THE ALARM STATE FOR COVID-19
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
ROCÍO TAMAYO BERMEJO, ARANZAZU LINARES ALARCÓN, CASILDA ORTEGA DE LA CRUZ, ISABEL MUÑOZ CASTILLO
Why was it done?
In the alarm state due to COVID-19 in March 2020, in order to reduce the number of visits to the hospital to outpatients who go to the Outpatient Pharmaceutical Care Area, a new Pharmaceutical Care and home delivery circuit is implemented.
What was done?
A circuit of Pharmaceutical Care and home delivery was implemented for outpatients in the alarm state due to COVID-19.
How was it done?
The needs, possibilities and resources of the Hospital were identified. Material resources were adapted: supply and stock management. A logistical solution was sought and a review of thermolabile drug stabilities was made. Human resources were restructured: definition of a new team, functions and responsibilities.
A new circuit was implemented with remote access. When the patient contacts, he´s attended by a pharmacist who performs the screening and interview (initiation/follow-up), who after reviewing the clinical records, validates the treatment and selects the dispensing process of the patient according to individualized. The preparation of shipments is organized through the use of a web resource, by a pharmacy technician and at a specific time, based on a list of shipments per day, dispensing sheets and personalized labels. Once the dispensations have been prepared, a double check is made by another pharmacy technician on a different shift.
Three phone lines and an email weren´t enough to attend to all concurrents demands in a period of less than 24 hours. To mitigate this situation, a multichannel information strategy was implemented to notify all patients.
Other limitations: incidents by the logistic operator, errors in addresses and incorrect dose shipments.
What has been achieved?
During two months (April-May), 1103 patients benefited from the new circuit, approximately 30% of the patients who collect medication in our Outpatient Pharmaceutical Care Area during this period.
What next?
The pharmaceutical care and home delivery circuit has been shown to be safe, and has been able to meet the needs that are required in a alarm state. Also, it´s a circuit applicable to other Pharmacy Deparments since it doesn´t require a large investment in resources.
HOME DELIVERY OF DRUGS, A DISPENSING SYSTEM THAT HAS COME TO STAY
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Ignacio Salar Valverde, Maria García Coronel, Consolacion Pastor Mondéjar, Mayte Gil Candel, Iris Muñoz Garcia, Carles Iniesta Navalon, Elena Urbieta Sanz
Why was it done?
This project was carried out to avoid the possibility of contagion by SARS-CoV-2 when going to collect the medication. The circuit began at the end of March and the month of April 2020.
What was done?
Send the hospital dispensing medication to the patient’s home.
How was it done?
The first step was to specify the patient was considered at risk for SARS-CoV-2, in the end, patients over 65 years of age or immunosuppressed were considered at risk.
The second step was what order to follow to select and evaluate candidate patients for home delivery, for which the solution was simple, it was decided to follow the order of the pharmacy agenda for the collection of medication. The SELENE® electronic medical record program was used to evaluate the patient’s risk.
The third step was to contact him by phone, to check if there was a possibility of collecting the medication by a family member / caregiver, and if not, confirm a delivery address.
The last step was the preparation of the medication in the proper conditions of conservation and identified with the name and address of the patient. Shipments were organized from the pharmacy service. Patients were given an appointment in the pharmacy agenda for the next shipment.
What has been achieved?
There were 139 home deliveries of medication, 47 in March and 92 in April. Around 139 telephone calls were made, they are not counted, not all patients could be contacted in the first attempt, and up to three attempts were made per patient.
The majority, 124 shipments, were made through the service that the hospital made available to them, except for 13 that were made through the Red-Cross and 2 through Civil-Protection.
What next?
Although the delivery of medication at home and was already carried out in some pharmacy services, because of the pandemic it has spread to the rest of the hospitals in our country.
This service should be maintained, despite its cost, for patients who meet a series of criteria, which must be established and agreed upon. In addition, a telephone follow-up should be carried out on the patients that we send the medication to their home.
Using in-house rapid quality control equipment to reveal morphine ampoule tampering – A case report
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Robert Baghdarsarian, Karin Hellström, Mattias Paulsson
Why was it done?
The health care providers at the Paediatric Emergency Ward discovered that when opening glass ampoules of morphine by snapping the top off, this did not result in the normal straight cut by the score. A close examination also revealed residual glue and the glass at the ampoule neck not being fully transparent. The sealed outer packaging also seemed manipulated for most of the morphine ampoules stored in the ward medication room. Simultaneously, staff discovered that one of the paediatric patients had not received the anticipated analgesic effect of the ordered morphine infusion.
What was done?
This case report describes how the compounding unit of Uppsala University Hospital (CU) was able to assist in analysing the contents of morphine glass ampoules and infusion solutions, in a case with suspected tampered containers
How was it done?
CU has invested in an easy-to-use spectrophotometer to check the concentration and identity of chemotherapy prepared in the clean rooms. The primary focus is to have an independent system to check preparations done by the chemotherapy robot e.g. in connection with software upgrades. This equipment was within hours adapted to be used for morphine analyses. The results clearly show that the infusion labelled 10 mg/mL was tampered with, containing only 0,4 mg/mL morphine. Samples were also sent to the Microbiological laboratory to check for risks for microbial exposure during infusion of tampered morphine.
What has been achieved?
CU was able to provide results of the contents of all ampoules, and the infusion solution administered to the patient, within a couple of hours and without any cost. The results showed that all ampoules had been emptied from its labelled contents and likely refilled with Sodium Chloride 9 mg/mL. The infusion solution given to patient was also likely prepared from a tampered ampoule. These results were crucial information in the conversation with parents about the incident, and the subsequent report to the police regarding the probable violence offence.
What next?
We recommend that all healthcare settings evaluate the possibility to collaborate closer with the hospital pharmacy, and in new ways.
Thanks to our CU being an integral part of the hospital with close interaction with wards, this rapid handling was possible to stage.
IMPLEMENTATION OF A TELEPHARMACY PROGRAMME TO HOSPITAL OUTPATIENTS DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
Pdf

European Statement
Selection, Procurement and Distribution
Author(s)
Rosalia Fernández-Caballero, Virginia Collados Arroyo, Clara Herranz Muñoz, Araceli Henares López
Why was it done?
Every month, an average of 700 patients receive pharmaceutical care in the outpatient consultation (OC) of our first-level hospital. Given the mobility restriction measures applied by the spanish government during the pandemic, access to this consultation was difficult for some patients. The aim of this program is to ensure the access to medication for all patients and prevent them and professionals to virus exposure. Telepharmacy program consists of providing pharmaceutical care based on available means of communication and access to medication through home drug delivery.
What was done?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we designed and implemented a telepharmacy programm to ensure access to medication for all patients.
How was it done?
Once weekly, the pharmacist contacted the listed patients during the following week in OC by telephone or via the hospital’s electronic platform, to offer the possibility of participating in the program. During teleconsultation, pharmacist provided the same attention as in face-to face consultation: administrative situation of the patient, adequate medical follow-up, assessment of adherence, review of interactions and adverse events and treatment changes. Moreover, we e-mailed the patient’s consent for home drug delivery by and external company. In case the patient didn’t have a web mail, we requested verbal consent. Once a week, one pharmacy technician prepared the medication and the selected company performed the home delivery in guaranteed storage conditions. To minimize the burden of work, the medication was sent for two months per patient. Oncohematological patients, who came to their doctor’s appointment every month, were excluded from this program.
What has been achieved?
Between March 20 and October 9, we have included 595 patients in this program and conducted 1190 teleconsultations and 872 home drug deliveries with a great satisfaction of outpatients.
What next?
Our next step is to improve the web system for sending alerts through our electronic platform to automate the home delivery process and thereby to reduce the logistic burden of the pharmacist and to increase the pharmaceutical care given to patients.

























