REDUCING MEDICATION WASTE IN HOSPITALS: DATA-DRIVEN SOLUTIONS AT THE SOURCE
Pdf

European Statement
Selection, Procurement and Distribution
Author(s)
Minke Jongsma, hospital pharmacist, Tjongerschans Hospital, Heerenveen, The Netherlands
Marja Bogaards, hospital pharmacist, Haaglanden Medisch Centrum, Den Haag, The Netherlands
Annemiek Zwetsloot, ICT consultant, Panacea Informatics, Oosterbeek, The Netherlands
Folkert Botma, ICT consultant, Panacea Informatics, Oosterbeek, The Netherlands
Why was it done?
A significant proportion of valuable medications, often produced far from where they are used, ends up discarded without ever being administered. Due to limited visibility into actual medication use, hospitals face challenges in understanding which drugs contribute to waste.
Analyzing internal data allowed us to gain insight into different aspects of medication waste. Addressing these aspects successfully improved sustainable use of medication.
What was done?
We developed a medication waste dashboard to promote sustainable decision-making across medication policies, purchasing, prescribing, distribution, administration, and waste management.
How was it done?
Daily, hospital pharmacies register all medication orders and dispensations (to patients or for stock), while nursing staff document actual administrations. The discrepancy between dispensed and administered drugs provides useful insight into unnecessary medication waste.
What has been achieved?
We integrated dispensing and administration data into a dashboard, offering real-time visibility at the organizational, departmental, ward, and drug group levels. This tool allows our multidisciplinary team to conduct trend analyses and implement greener practices. Key outcomes include: 1) reduction of medication waste, 2) preventing excessive stock accumulation, 3) optimizing internal processes, and 4) maximizing reuse. Additionally, these data supports effective management during drug shortages and provides critical insights into missing opioids.
What next?
Utilizing data allows us to retrospectively analyze trends and project future scenarios, unlike traditional waste-bin audits. This data-driven approach empowers us to make proactive adjustments, guiding hospitals toward long-term medication waste reduction and facilitating benchmarking across healthcare institutions.
OPTIMISING PATIENT ADHERENCE IN HEART TRANSPLANTATION: A PHARMACIST-LED EDUCATIONAL APPROACH
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Lucie Malečová, Daniela Seberová, Blanka Zelená, Markéta Hanulíková, Kornélia Chrapková, Stanislav Gregor, Michal Hojný
Why was it done?
Adherence to immunosuppressive medication is crucial for long-term graft survival. Patients receive substantial information from various healthcare professionals regarding new medications and lifestyle choices during hospitalisation and post-discharge. Frequent non-adherence indicated that the existing educational approach led by physicians was insufficient. Our objective was to create optimal conditions for providing these instructions to patients before discharge.
What was done?
In collaboration with the cardiology department, hospital pharmacists created and implemented a new educational project to improve adherence among heart transplant patients. The main activity involves hospital pharmacists conducting educational visits at the patient’s bedside, supported by new educational brochures, materials, and questionnaires.
How was it done?
We created a questionnaire and collected baseline data by assessing the knowledge of transplant patients educated by the existing educational approach. Afterwards, we designed and implemented a six-visit educational program and prepared new educational materials and brochures. A new record system was integrated into the hospital information system to facilitate communication between doctors and pharmacists, documenting educational visits and questionnaire results. The initial three visits, scheduled during hospitalisation, cover the correct use of immunosuppressants and other medications, their interactions, and potential adverse effects. Guidance on recommended lifestyle changes post-transplantation, such as hygiene, diet, and infection prevention, is also included. The remaining three visits occur within one year post-discharge to assess patient knowledge with the previously mentioned questionnaire and adherence to the treatment plan with BAASIS©. During these visits, the pharmacist conducts a comprehensive review of adherence, addresses any drug-related issues, and guides medication changes.
What has been achieved?
Since the project’s initiation, 120 visits have been completed, involving more than 30 patients. The education significantly improved patient knowledge, with educated patients scoring an average of 94% correct answers on the knowledge questionnaire compared to 59% correct answers of patients educated by the existing educational approach. Only three educated patients were non-adherent, with the most common type of non-adherence being failure to take medication at the prescribed time.
What next?
As more patients participate in the project, we aim to correlate their knowledge and adherence with tacrolimus levels and the incidence of rejection. Additionally, we intend to extend this educational initiative to other departments within the hospital.
Collaborative network between healthcare settings: hospital and community pharmacy
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Carmen Redondo Galán, Cristina Ortega Navarro, Ana de Lorenzo Pinto, Beatriz Torroba Sanz, Cecilia Martínez Fernández-Llamazares, Silvia Manrique Rodríguez, Álvaro Narrillos Moraza, Carmen Rodríguez González, Ana Herranz Alonso , María Sanjurjo Sáez
Why was it done?
Transitions of care put the patients at risk for medication error as a result of poor communication and information loss. Treatment beginnings, complex treatment and medication reconciliation errors are an important cause of morbidity and have a predominant role in chronic complex patients (CCP). In this sense, collaboration and effective communication between hospital and community pharmacy are considered essential elements to guarantee continuity of patient care, obtaining better health results in terms of safety, effectiveness and efficiency.
What was done?
Create and implement a collaborative network with direct communication between the Hospital Pharmacy Service of a tertiary hospital and the community pharmacies responsible for patient follow -up.
How was it done?
A multidisciplinary group of hospital pharmacists dedicated to different clinical areas was created: three pharmacists from the Emergency Department, two from the Paediatrics Department, one from the Neurology Department and one from the Outpatients area. They selected and contacted by telephone the 40 community pharmacies responsible for 25% of patient prescriptions in the area. Periodic meetings were scheduled and possible strategic lines of collaboration were shared. The following priority groups were identified: Group 1: CCP (paediatric patients and fragile elderly patients) and Group 2: patients treated in the hospital emergency department. We addressed logistical aspects (supplies and preparation of formulations), pharmacotherapeutic monitoring (adherence, adverse drug reactions and collaboration in the management of CCP). The main limitations were small population and short follow-up time.
What has been achieved?
From March 2023 to September 2023, the hospital Pharmacy Service has received 50 consultations on 45 patients from community pharmacies: 85% were classified as group 1 and 15% group 2. Pharmaceutical interventions were related to medical shortages (28%), reconciliation errors at discharge (22%), information about formulations (20%), information about new treatments (15%), prescribing errors (12%) and adverse drug reactions (3%). Community pharmacists appreciated accessibility and value of information provided by hospital pharmacists. 50% of patients avoided a hospital visit to solve their queries.
What next?
Our first results show the importance of pharmacist interventions with patients and other healthcare professionals.This collaborative network can be applicable to all services that work with community pharmacies to guarantee greater coordination and integration in the different healthcare settings.
Redispensing of expensive oral anticancer medicines: a practical application
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Why was it done?
OAM are widely used in the treatment of solid tumors and are administered orally in cycles that require self-administration at home. However, dose adjustments and discontinuations often lead to leftover medication which is discarded as waste. Therefore, the increasing use of expensive OAM comes with the downside of a financial and environmental burden. To reduce this waste, returned OAM to the pharmacy could be considered for redispensing to other patients providing guaranteed quality.
What was done?
We defined quality criteria for redispensing of oral anticancer medicines (OAM) in our hospital pharmacy. These criteria were laid down in a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) to assess the eligibility for redispensing of returned OAM. This SOP was implemented in daily pharmacy practice.
How was it done?
A systematic risk analysis was conducted to determine eligibility of OAM for redispensing taking relevant guidelines and product information into account. The defined quality criteria were translated into a SOP and implemented in daily pharmacy practice. Over a year period, the number of returned OAM accepted for redispensing was quantified, and the reduction in financial waste and environmental burden calculated.
What has been achieved?
From the systematic risk analysis, four categories of quality aspects were identified: product presentation suitability (stability characteristics, storage requirements), physical condition (unopened or opened secondary or primary packaging, visual appearance), authentication (Falsified Medicines Directive, confirmation of initial dispense, recall), and additional aspects (remaining shelf life, period of storage under uncontrolled conditions). The first category identified that in principle, 75% of the licenced OAM (n=..products) dispensed at our institute is eligible for redispensing. From all combined quality aspects, a flow chart was created according to which each individual returned OAM is assessed . During the study period, 10,415 OAM dose units out of 13,210 returns (79%) were accepted for redispensing. The total value of OAM accepted for redispensing was €483,301, accounting for 0.9% of the total value dispensed during this period. Furthermore, the potential reduction in environmental burden was estimated at 1132.1 g of potent active pharmaceutical ingredient.
What next?
We established an easily implementable, comprehensive quality assessment of returned OAM for redispensing. Wide implementation of this approach would result in serious OAM cost and waste reduction.
RutiCar: an outpatient medication dispensing point
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Why was it done?
This service emerged as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, when the collection of hospital medication posed patients, many of whom were immunocompromised, at higher risk for COVID-19 and other infections, as they had to enter the hospital facilities. Over time, it was observed that this service was not only beneficial during periods of high SARS-CoV-2 transmission. RutiCar enabled medication pickup from the patient’s own private vehicle, avoiding necessity for parking as well as entering the hospital.
What was done?
In June 2021, the Pharmacy Department of Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital(HUGTP) established an outpatient medication dispensing point located outside the hospital premises, “RutiCar”. This initiative facilitated patients in collecting their chronic treatments without entering the hospital, enabling direct access from their vehicles.
How was it done?
A new preparation and dispensing circuit was established. The patients specify their preferred date for medication pickup by telephone, e-mail or by a form after scanning a QR code. Pharmacy technicians undertake the responsibility of scheduling the appointment and preparing the medications one day prior to the designated dispensing day. The prepared medications are transported early in the morning to a temporary medication storage facility situated within the hospital’s parking area. Finally, the patient arrives at RutiCar at their scheduled appointment time and, without the need to exit their vehicle, collects their medication.
This service is aimed at patients with chronic treatments who have been on their medication for an extended period (>6 months) and show adherence. Pharmacists play an important role in this context, by ensuring that patients meet the criteria to initiate RutiCar service, reviewing treatments to validate their continuation and overseeing medication pickups to enhance patient adherence.
What has been achieved?
This service has led to an improvement in the medication dispensing process, assisting 10.46%(282) of the monthly average of patients who collect hospital medication(2695) and extending the hours for medication pickup, facilitating the work-life balance for patients and enhancing access to patients from remote areas.
What next?
In the future, improvements can be considered, such as implementing reminders for patients who have not yet scheduled their appointments and are projected to run out of medication soon, or automated appointment systems.
Medication waste in a hospital setting; counts, concerns and considerations
Pdf

European Statement
Selection, Procurement and Distribution
Author(s)
Minke Jongsma, Marja Bogaards
Why was it done?
The use of medication is related to almost one-fifth of the total CO2 emission caused by the public health sector. Conservative estimates reveal that the amount of medication distributed by public pharmacies but wasted (thrown away unused) by patients in the Netherlands equalizes a total amount of 100 million euro. Data regarding medication waste in Dutch hospitals is not yet available.
What was done?
We analyzed the stream of medication waste in our hospital and tried to reduce this by addressing the main causes.
How was it done?
In our hospital setting, medication for each in-hospital patient is distributed daily for the next 24 hours by the hospital pharmacy. All unused medication is returned to the hospital pharmacy. We quantified and analyzed all returned unused medication in our hospital on 9 separate days.
What has been achieved?
On average, 27,9% of all medication distributed to in-hospital patients is daily returned to the hospital pharmacy. The largest part of this returned medication, 83.5% (23.3% of all medication distributed to in-hospital patients) is wasted daily. This equalizes a total amount of 87.500 counts yearly, representing a value of 41.000 euro. In terms of waste, 60 medical waste bins of 50 liter (a total volume of 3000 L) are needed to dispose of this medical waste.
Analysis of the main causes reveal that distributing both parenteral medication and medication prescribed ‘as needed’ to in-hospital patients contribute largely to medication waste, as well as the inability to adequately anticipate on the discharge of patients.
What next?
By addressing the main causes we can decrease medication waste by 45%. Further reduction can be achieved by considering re-uptake of returned medication in our main stock. Our medication distribution process, however, is mainly based on financial and quality based decisions, which excludes re-uptake. But should impact on planetary health not also be considered? To realise this, though, both ecotoxicologic data as well as information related to environmental impact of medication production should be available and easily accessible.
Development of an oral ketamine: compounding and creation of a pharmaceutical care circuit for phantom limb syndrome
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Javier Corazón Villanueva, Natalia Sanchez-Ocaña MartínPast, Virginia Puebla García, Lidia Ybañez García, Maria De la Torre Ortíz, Paloma Pastor Vara, Maria Fernandez-Vazquez Crespo, José Manuel Martínez Sesmero
Why was it done?
The PLS is the perception of a non-existent limb that may occur in up to 80% of amputees. The management of this syndrome is complex and alternative drugs are sometimes used for the treatment. The absence of a marketed formulation, off-label use of drugs and the complex treatment of pain make the role of the pharmacist essential.
What was done?
Development and validation of an oral ketamine compound and a specific pharmaceutical care circuit (PCC) as a part of the treatment of phantom limb syndrome (PLS).
How was it done?
A literature search was carried out on the preparation of this compounding, as well as on the use of oral ketamine (bioavailability, dosage, adverse reactions).
An oral solution of 10mg/ml was prepared (final volume 50ml: 500 mg of injectable ketamine solution or raw material, 20 ml of simple syrup with a sufficient amount of purified water and 2 drops of lemon essence). To establish the expiration date recommendations of Good Manufacturing Practice Guideline were followed and the organoleptic characteristics were evaluated for quality control.
The PCC created consists of the following stages:
1. Setting up a first presential visit to provide pharmaceutical care during admission: to inform the storage conditions, most common adverse effects and recommendations about medication intake.
2. Dispensing at discharge and initially appointments every 7 days for a closer follow-up: control of adverse reactions (confusion, agitation, nausea, etc.), monitoring of the appropriate use of ketamine and other analgesic medication (avoiding possible abuse and addictive behaviour) and pain control. Pharmaceutical interventions are communicated to the pain management unit (PMU).
3. Spacing of visits fortnightly once the treatment is well-stablished and proposing a telepharmacy service.
What has been achieved?
The ketamine formulation developed has been used in our hospital in three patients with satisfactory results. The interventions carried out were: pain control problems, possible inappropriate use, reduction in the number or dosage of concomitant medication or ketamine itself.
What next?
The capacity to provide therapeutic alternatives and a more exhaustive pharmacological control of pain in collaboration with the PMU can improve the safety and effectiveness of these treatments.
Measures taken in hospital management following the impact of the coronavirus pandemic.
European Statement
Selection, Procurement and Distribution
Why was it done?
The aim of the study is to assess the crisis impact on the consumption of pharmaceutical products in the intensive care unit in order to estimate, rationalize the need and prevent supply problems.
What was done?
Due to Covid-19 pandemic and its major economic impact, we carried out a comparative study of the consumption of pharmaceutical products in the intensive care unit before and during the crisis.
How was it done?
A list of pharmaceutical products to be evaluated has been established beforehand. The choice was made for the products most used in intensive care units in accordance with the recommendations of COVID management. The list includes drugs and medical devices.
In order to compare the consumption of these products in terms of quantity and cost, data collection was carried out over two periods, each of 6 months, before and during the crisis in Tunisia. The first from January 1st, 2019 to June 30th, 2019, the second from January 1st, 2021 to June 30th, 2021.
What has been achieved?
As a result of this assessment, it was possible to quantify the increase in several drugs and medical devices. It led us to:
-modulate our supply of these products
-take rationalization measures in cooperation with doctors
-develop management protocols according to the recommendations and available products
– close monitoring of prescriptions and compliance with protocols in order to optimize consumption, avoid any abuse and limit breaks as much as possible.
Tab. Variation of consumption and cost
Product Consumption2019 Consumption2021 Variation factor of the consumption Variation factor of the cost
Hypnotic curares 25 170 6.8 8.1
Antithrombotics 647 2286 3.5 8.1
Antibiotics 932 4060 4.4 11.2
Fluconazole 240 378 1.6 1.9
Dexamethasone 845 1268 1.5 2.0
Isolation gown 740 6925 9.4 7.8
Masks 6100 13300 2.2 2.2
hydroalcoholic products 123 217 1.8 1.8
What next?
A generalization of the drafting and updating of the protocols concerning the management and the dispensing is programmed for all the other departments which will be validated by the therapeutic committee and the antibiotics committee.
OPTIMIZATION AND CENTRALIZATION OF THE HANDLING CIRCUIT OF HAZARD DRUGS FROM THE PHARMACY SERVICE
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Mireia Iglesias Rodrigo, Júlia Pardo Pastor, Alba Manzaneque Gordon, Cristina Sangrador Pelluz, Núria Meca Casasnovas, Clara Sebastián Carrasco, Fernando Salazar Gonzalez, Gemma Garreta Fontelles, Jordi Nicolás Picó
Why was it done?
Due to the risk posed by the handling of Hazard Drugs (HD) in the healthcare field, it is necessary to implement circuits that guarantee the professional’s safety.
What was done?
Create an internal classification of HD based on the NIOSH List of Hazard Drugs in Healthcare Setting 2020, to optimize the circuit of its handling from its receiving to its administration.
How was it done?
Considering the HD included in the Pharmacotherapeutic Guide (PTG) of our center, the stages of reception and adaptation/preparation/dispensing/administration and other precautions were analyzed.
Categories were established, analyzing the needs of each stage according to: NIOSH level of danger, setting (inpatient/outpatient), pharmaceutical form, commercialized pharmaceutical specialties or available alternatives, and material/personal resources.
Prior to its implementation, e-learning training was carried out for the healthcare professional involved.
What has been achieved?
A total of 25.3% (379/1498) of the pharmaceutical specialties included in PTG were HD. Thirteen HD groups were identified. Due to the fact that in the outpatient setting the drug is dispensed to the patient in its original container, the actions implemented were only carried out for inpatients, representing these 9/13 of described groups. The established training was carried out by the 89% of professionals. Proposed measures for HD are summarized in Table 1.
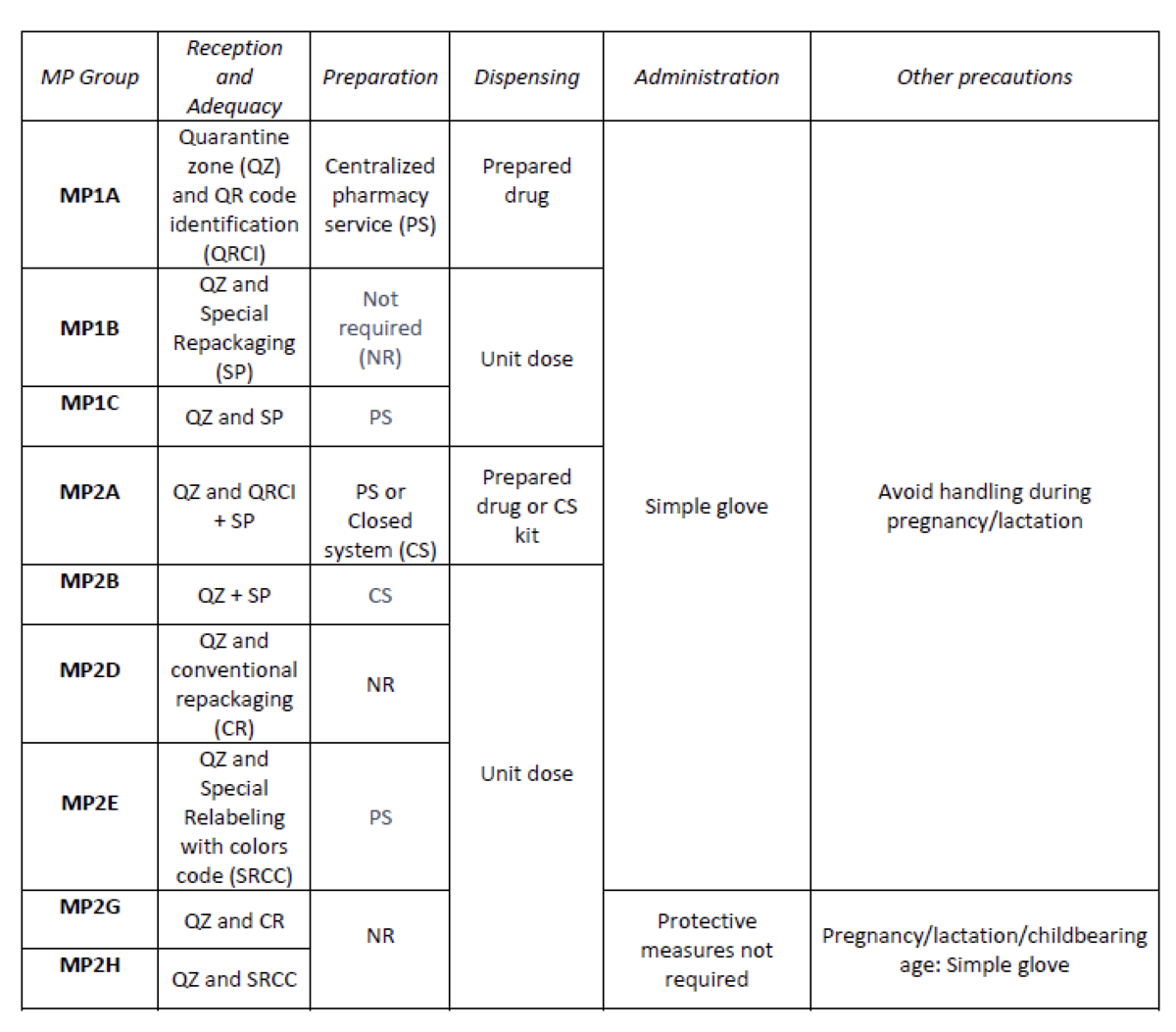
What next?
Monitoring and evaluation of the circuit
Case-study: Pharmaceutical teleconsultation using a mobile application
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Joana Russo, Maria João Ribeiro, Humberto Gonçalves, Joana Ribeiro, Silva Cristina, António Gouveia
Why was it done?
In our country the oncology medication for ambulatory patients is dispensed by the hospital pharmacist (HP). Due to several aspects (i.e., COVID-19 pandemic) the process of distribution of said medication has changed in that the HP and the patient no longer meet face to face (Drive-thru systems, proximity projects in which the medication is sent to a nearby pharmacy of the patients living area). A tool was required that enabled the HPs to continue to monitor the relevant clinical aspects (patient education; medication adherence (MA), drug interactions (DI) and adverse events (AE) evaluation).
What was done?
We used a mobile application (App) to conduct the pharmaceutical evaluation of clinical aspects that need to be considered when dispensing oncology medication.
How was it done?
In collaboration with the Information Technologies department of our hospital, an App was developed. It integrates the patient’s hospital prescriptions and their answers to an adaptive query that identifies cases that need further clinical data We selected a specific drug (ibrutinib) and developed an algorithm that presented the extended questions accordingly. The App was announced to patients that required hospital medication and wanted to receive it through an alternative method of distribution.
What has been achieved?
In little over a year, a total of 1720 requests were received (668 patients). The algorithm was successful in differentiating patients whose evaluation needed to include additional clinical information. In 22 requests, further data was automatically gathered (9 patients) enabling us to evaluate MA, DI and AE. These teleconsultations do not require additional professionals (ie an assistant to register the request) nor a compatible time slot for a pharmacist-patient phone call.
What next?
The results showed that the concept of pharmaceutical teleconsultations through an App is viable and we intend to extend its range to other drugs and to dissociate the teleconsultation from the dispensing request. This approached also showed that proximity between HP and patients was positively affected allowing patients to consult their hospital pharmacist whenever they need to and wherever the patient was.
























