MEDICATION REVIEW IN FALL-RELATED HOSPITAL ADMISSIONS
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Why was it done?
Falls in older people are a significant public health problem due to their high prevalence, the injuries they cause and the associated economic burden. They are often caused by multifactorial risks, being the Fall-Risk-Increasing-Drugs (FRIDs) one of the most significant ones. The aim of this initiative is to reduce FRIDs prescriptions among elderly at risk of falling, by assessing their individual Benefit-Risk Balance.
What was done?
A circuit was designed and implemented to review and optimize the medication of patients admitted to hospital after a fall.
How was it done?
On an everyday basis, the Health Management Unit of our tertiary university hospital sends a list of fall-related hospital admissions to the clinical pharmacists (CP), who review those patients’ medication and identify FRIDs (drugs affecting central nervous system, hypoglycemic/antihypertensive agents, among others). Electronic Health Records (EHR) are consulted to evaluate if medication could have had a role in those falls. When a patient’s medication is subject to any optimization, CP contact the referring physician to propose therapeutic modifications. This pharmacist-doctor communication is carried out during the hospitalization period in case of Internal Medicine admissions and by an administrative appointment with the primary care physician (PCP) when patients are admitted in other units, such as Traumatology or Neurosurgery. The PCP evaluates the medication review report attached by CP in patients’ EHR and modifies medication if necessary.
What has been achieved?
Between May and September 2021, 114 patients were admitted to hospital due to a fall. After excluding 10 institutionalized patients (pharmaceutical care provided by their own team), 6 patients having fallen after alcohol consumption or intentional drug overdose, and 7 palliative patients, the medication of 91 patients was reviewed. The mean age was 80 and the 64.8% were female. An average of 3 FRIDs was identified per patient. 52 pharmaceutical interventions were made, mainly dose reductions and FRIDs deprescribing suggestions.
What next?
This initiative is feasible and potentially beneficial for patients’ health care. Medication review leads to the identification of not only FRIDs, but also different drug related problems. We look forward to assessing the impact of our practice in terms of interventions accepted; drug-related negative outcomes avoided and decreased hospital readmissions.
OPTIMIZATION OF DRUG MANAGEMENT
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Why was it done?
To avoid stock breaks by ensuring at all times the existence of the medicines included in a 2nd level hospital.
What was done?
Optimization of medication management in a Hospital Pharmacy Service (HPS) through the development and use of a purchasing planner.
How was it done?
One obstacle we encountered was knowing the inventory in real time. This required a computer program for stock management, human resources or intelligent warehouses to enable real-time inventory control.
After the training, learning and updating of working procedures, an analysis of the consumption of the drugs included in the pharmacotherapy guide was carried out in order to calculate the minimum stocks, safety stocks, maximum stocks and order points.
Data were loaded into the management software and parameters were defined so that when a drug reached the point of order a purchase proposal would be made until the maximum stock was reached.
What has been achieved?
In February 2020, the purchasing planning system was implemented. The planner’s lists were parameterized to organize the drugs by therapeutic groups or areas of interest within the HPS. In addition, communication among all professionals was enhanced for rapid response to a lack of medication and a periodic inventory counting plan was designed to ensure adequate stock.
After changes, more than 80% of HPS medications are ordered through purchasing planning, reducing stock breaks due to never reaching the safety stock of selected drugs.
What next?
This system is applicable to all HPS that has the same management software. It is necessary to have an optimization system in the drug management to ensure their real stock in the hospital environment and their availability for patients.
Proactive pharmacovigilance program of Covid-19 vaccination in haemodialysis centers
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Carla Pinto, João Godinho, Luzia Fernandes, Patricia Vieira, Isabel Ferreira, Inês Sousa, Carolina Vieira, Ana Sardinha
Why was it done?
To promote a more effective notification process than the spontaneous reporting of suspected adverse drug reactions and contribute to the knowledge of the safety profile of medicines.
Covid-19 vaccines are medicines under additional monitoring, labelled with a black inverted triangle and expected to play a major role in the control of COVID-19 pandemic due to SARS-Cov2 virus.
This new medicine was administrated in a short time period and simultaneously to a large number of individuals in the beginning of vaccination period in Portugal (January 2021), to patients and healthcare professionals of our haemodialysis centers.
What was done?
Development and implementation of a proactive pharmacovigilance program to identify suspected adverse drug reactions (ADRs) to a covid-19 vaccine administration in haemodialysis centers patients and healthcare professionals.
How was it done?
Maintaining spontaneous report for immediate suspected ADRs, pharmaceutical services developed a form to collect suspected ADRs in the following 7 days after each dose administration. It was applied to each vaccinated exactly 7 days after the administration of each dose. To simplify its filling and application, overcoming workload and lack of resources in this pandemic setting, information was displayed with check mark boxes, including the list of described ADRs sorted by frequency, duration intervals and blank space for unexpected reactions.
Due to the large amount and variability of individuals and centers, the form was distributed in paper and online formats and applied to vaccinated patients by doctors or nurses.
Pharmacists validated the forms to notify the national pharmacovigilance system for serious or unexpected ADRs.
What has been achieved?
From the 9469 covid-19 vaccine administrations we obtained 6962 filled forms (74% of vaccinations) from which 38% (2666 forms) had suspected ADRs. 2nd dose had a lower participation rate of about 10%. These participation rates where due to no filled forms in cases of no symptoms.
What next?
Apply this proactive pharmacovigilance model in the integration in the institution of future medicines under additional monitoring will allow better knowledge of occurrence of adverse reactions, improving safety of medicines.
For the best outcomes program must be adapted to each medicine’s specification, considering even simpler tools to obtain information when there are no symptoms to report.
Active Pharmacovigilance of COVID-19 vaccines
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Manuela de Sousa, Ana Catarina Felismino, Ana Rita Pereira, Ivone Máximo, Liliana Pedro, Natacha Santos, Paula Campos
Why was it done?
Vaccines against COVID-19 are classified as “Medicines subject to additional monitoring” by the European Medicines Agency, making it essential to implement active pharmacovigilance systems that allow for the rapid identification of new safety information.
What was done?
Active surveillance of the COVID-19 vaccination process of health-care professionals and immunoallergy patients of our hospital.
How was it done?
By proposal of the Pharmacy Service, a multidisciplinary Pharmacovigilance Committee composed of two Pharmacists, two Physicians and two Nurses was created. The vaccinated professionals and patients were periodically identified, with the support of the Occupational Health and Immunoallergy Departments. Questionnaires to identify Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) were created in Google Forms® for each COVID-19 vaccine brand and sent to health-care professionals´ institutional email address, or to the email patients provided in the signed informed consent. The responses were exported to an EXCEL® database, analyzed by the Pharmacovigilance Committee, the ADRs identified and communicated to the regional Pharmacovigilance Centre.
What has been achieved?
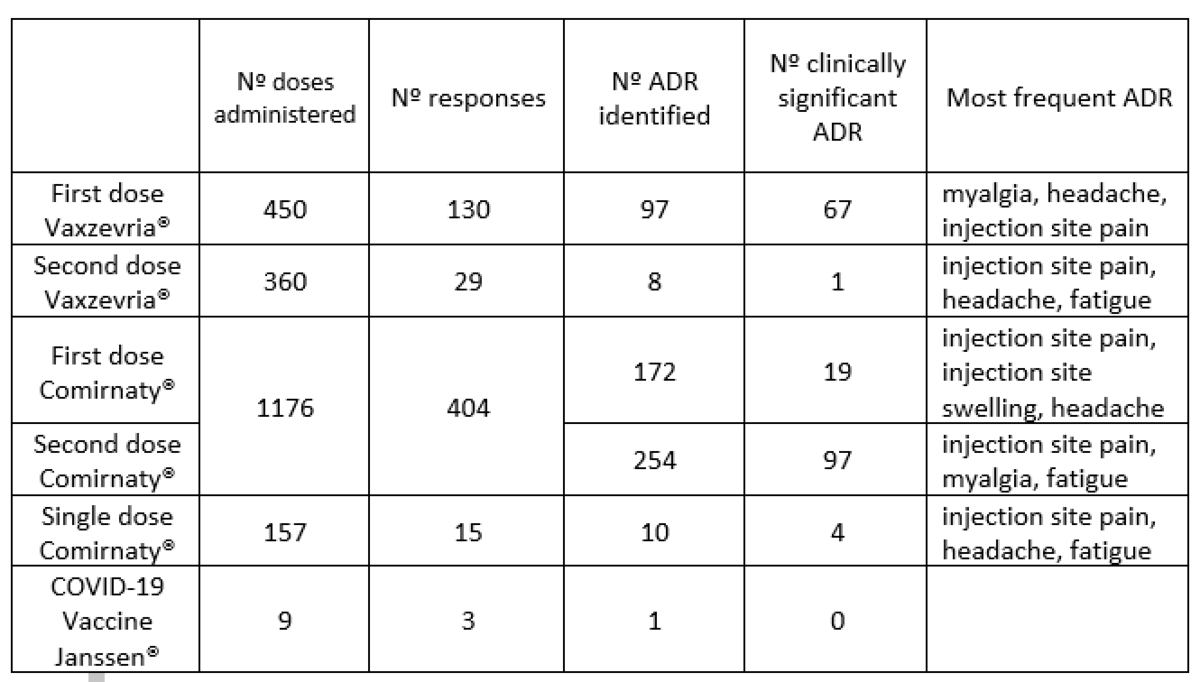
From 29 December 2020 to 31 August 2021 a total of 2141 questionnaires were sent, 578 responses were obtained and 542 ADRs were communicated to the regional Pharmacovigilance Centre. No anaphylactic reactions were reported. Nº doses administered Nº responses Nº ADR identified Nº clinically significant ADR Most frequent ADR First dose Vaxzevria® 450 130 97 67 myalgia, headache, injection site pain Second dose Vaxzevria® 360 29 8 1 injection site pain, headache, fatigue First dose Comirnaty® 1176 404 172 19 injection site pain, injection site swelling, headache Second dose Comirnaty® 1176 404 254 97 injection site pain, myalgia, fatigue Single dose Comirnaty® 157 15 10 4 injection site pain, headache, fatigue COVID-19 Vaccine Janssen® 9 3 1 0
What next?
Increase awareness of the importance of Pharmacovigilance amongst hospital health-care professionals to combat sub-notification of ADRs. We also plan to extend this active Pharmacovigilance program to other medicines in use at our hospital.
Implementation of an artificial intelligence tool for the detection of drug safety problems
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Noe Garin, Laia Lopez-Vinardell, Pau Riera, Adrian Plaza, Ivan Castellvi-Barranco, Jose Mateo-Arranz, M. Antonia Mangues
Why was it done?
APS is a rare disease with a high risk of thromboembolism. Recently, some data suggested an increased risk of thrombotic events with direct-acting anticoagulants (DOAC) compared with vitamin K antagonists in APS. Some agencies advise against the use of DOACs in these patients.
This methodology can be extrapolated to other risk situations, so this was a first step with AI to further detection of safety issues.
What was done?
We implemented an Artificial intelligence (AI) tool based on natural language processing (SAVANA®) to identify patients at risk of thromboembolism, defined as Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) diagnosis treated with direct-acting anticoagulants (DOAC). SAVANA® is an AI tool able to extract information contained in free-text from electronic clinical records.
A prior operation work was conducted, involving: direction, pharmacy, documentation, IT, SAVANA®, data protection. The work and previous meetings evaluated: feasibility, previous requirements, privacy issues, IT involvement and contract signings.
How was it done?
The implementation consisted of:
– Transference of medical record information to the SAVANA® cloud.
– Identification of the health problem (APS) and initial search.
– Search algorithm optimization in a multidisciplinary team.
– Evaluation of the search by SAVANA® by peer review in a sample of randomly selected cases (n=200).
– Precision and sensitivity analysis. Algorithm improvement.
– Obtaining the Gold Standard and validation.
– Definitive search for the detection of patients with APS in treatment with DOACs and performance of interventions.
What has been achieved?
The project implementation is at a very advanced stage. The algorithm has currently been evaluated and is being refined after precision and sensitivity analysis. Final validation and definitive identification of patients at risk is expected at the end of 2021. Patients detected during the implementation method have been evaluated with the haematology team.
What next?
This methodology can be implemented in any centre with computerized medical records. The use of AI is the only tool available for the identification of certain groups of patients when health problems are not coded. In other cases, its use regarding the extraction of lists allows a great capacity for analysis, absence of biases derived from human error, guarantee of reproducibility and complementary data obtention, mainly in samples of high size.
A pharmacist-led pharmacovigilance initiative for the first Austrian Covid-19-vaccination campaign
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Nikolaus Lindner, Katharina Heitzeneder, Nora Hummer, Elisenda Pichler, Doris Haider
Why was it done?
Due to the lack of long-term safety data, the principal goal was to assure a safe and effective use of the available vaccines by coordinating stringent logistical operating procedures as well as by facilitating early detection and evaluation of possible safety signals. A further objective of this initiative was to increase the awareness among healthcare workers regarding the possible health risks associated with a SARS-CoV-2 infection and Covid-19 vaccines as preventable countermeasures.
What was done?
A Covid-19 vaccination pharmacovigilance campaign was implemented in a clinical setting with the focus on patient safety and quality assurance as part of an employee vaccination rollout. The pharmacy department set up a pharmacovigilance service-point to assess vaccine safety as well as potential adverse events and assure patient care by close follow up.
How was it done?
Assessing and reacting to individual safety signals on time represented a critical challenge. Pharmacists designed questionnaires capturing possible adverse events. In order to lower the barriers for participation it was decided to take a paper-based approach instead of electronic distribution. A pharmacovigilance service-point was continuously managed by two pharmacists directly at the vaccination site to achieve a high response rate. Throughout the campaign the completed questionnaires were simultaneously evaluated, as rapid action was key to detect safety signals early and implement measures accordingly.
What has been achieved?
The results showed a high response rate to the questionnaire of 95% and 53% after the first and second dose, respectively. A significant increase of symptoms after the second dose compared to the first dose reflected the findings of the marketing authorisation study. Based on the analysis no further safety precautions were needed. However, appointments before night or weekend shifts had to be discouraged as well as the vaccination of the whole staff from one department on the same day. As a result, disruptions to patient care could be avoided successfully.
What next?
This initiative serves as a valuable model for upcoming vaccination campaigns and especially for pharmacovigilance projects aiming to assess adverse events of recently approved medicines. Moreover, the successfully implemented multi-disciplinary approach represents the basis for further hospital-wide pharmacy projects and may facilitate the implementation of pharmacist-provided vaccination services.
IMPLEMENTATION OF ASSISTED ELECTRONIC PRESCRIPTION IN THE OUTPATIENT AREA
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
JUDIT PERALES PASCUAL, HERMINIA NAVARRO AZNAREZ, ANA LOPEZ PEREZ, LUCIA CAZORLA PODEROSO, IRENE AGUILO LAFARGA, ANA PEÑAS FERNANDEZ, Mª REYES ABAD SAZATORNIL
Why was it done?
Despite the volume of patients seen at UPEX, the complexity of care and the cost of the treatments, in 2019 the prescription was transcribed by pharmacists with the consequent risk/investment of time that this entails. The aim was to incorporate organizational/technological changes that would improve the safety and quality of pharmaceutical care.
What was done?
An outpatient is a patient who goes to the outpatient unit of their Hospital Pharmacy Service (UPEX) to collect a drug for hospital use/diagnosis or foreign drug (it will be administered without health personnel intervention).
We collaborated in the design and validation of the PresSalud®(Dominion®) program, developing the implementation of assisted electronic prescribing (AEP) as an objective in the SAMPA project (Registration and Promotion Service for Adherence to Medications for Elderly Patients).
How was it done?
Access from the electronic medical record to the prescription, the integration of the latter with the dispensing program and the latter with the pharmacy item program guarantees an increase in the safety of medication use by incorporating clinical decision aids.
Different prescription assistance protocols were developed. Presentations and sessions were given to hospital doctors explaining how to prescribe through PresSalud® adapting them to the different services implemented with AEP.
What has been achieved?
In 2018, the AEP was implemented in the infectious, digestive, dermatology, rheumatology, neurology and hematology service (only in hemophilia consultations). Between May-September 2020, it was expanded. It is currently 92.3% implemented and 100% is expected by the end of 2021 (with the rest hematology consultations).
Currently, the percentage of prescriptions to outpatients using AEP with respect to the total prescriptions in this area is 83%; this increase contributes to avoid errors in transcription and to reduce the time spent in checking the prescription, providing greater safety in the use of the medication and better patient care which translates into higher quality of care.
What next?
The implementation of the AEP guarantees safe and efficient prescription; in short, the organizational/technological changes that this entails contribute to improving the quality of pharmaceutical care received by the patient. The proposed solution can be easily extended to other hospitals implementing AEP.
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN APPOINTMENT MANAGEMENT MODULE APPLIED TO THE OUTSIDE PATIENT AREA
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
JUDIT PERALES PASCUAL, ANA PÉREZ LÓPEZ, HERMINIA NAVARRO AZNAREZ, ELENA HERRANZ BAYO, MARIA PEREZ MORENO, CARLOS-IGNACIO DIAZ CALDERON HORCADA, Mª REYES ABAD SAZATORNIL
Why was it done?
In 2019 the UPEX attended a large volume of patients without a scheduled appointment, long waits were generated and the pharmacotherapeutic follow-up was complicated. The purpose was to implement an appointment management module to avoid crowds, excessive waiting times, allowing better organizational management of care and knowledge of patients in each type of consultation.
What was done?
An outpatient is a patient who goes to the outpatient unit of their Hospital Pharmacy Service to collect a drug for hospital use/diagnosis or foreign drug (it will be administered without health personnel intervention).
An appointment management system was implemented in accordance with the objectives of the SAMPA project (Service for Registration and Promotion of Adherence to Medicines for Elderly Patients), included in the European STOPandGo project.
How was it done?
Creating a cross-cutting system for the entire clinical circuit from prescription to dispensing involved a great deal computer involvement. Although it began to be used in November 2018, it was not used by the mostly part of prescribing doctors until the end of 2020.
Now, when the patient leaves medical consultation, he/she will go to the pharmacy and will be seen by a pharmacist. Besides, the program will propose a return appointment when it calculates that the patient has a week’s worth of medication, thus preventing the patient from running out of medication. The pharmacist will decide if the patient needs pharmacotherapeutic follow-up.
What has been achieved?
In 2019, 5 services cited patients while in 2020 it was 14; the percentage of patients attending pharmacy cited increased from 73.2%(2019) to 79.4%(2020).
Currently, the pharmacist knows in advance which scheduled patients he has and can establish a better organizational care management and determine in advance if the patient needs a close pharmacotherapeutic follow-up. Additionally, with this system an average waiting time of 03:55min was achieved (in 2019 appointments with waits >30min were recorded).
What next?
The implementation of the appointment management system has made possible to achieve better organizational management of care,avoid crowds,excessive waiting times, and provide better patient care and pharmacotherapeutic follow-up. The proposed solution can be extended to other hospitals.
Applying novel technologies to advance hospital pharmacy practice
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Why was it done?
As we venture into the 2020s, health-system pharmacies need to consider these novel approaches to deliver pharmaceutical care to their patients given the changing population needs, lifestyles, and available home technologies accessible to most patients. The ultimate goals are to enhance patient safety, increase hospital pharmacy operational efficiency, and maximize revenue.
What was done?
Novel technologies were implemented at Houston Methodist to enhance patient safety and experience. These include voice-activated devices in patient rooms, smart glasses for pharmacists, smart phones for hospital pharmacy service provision, artificial intelligence, and tele-health
How was it done?
Careful infrastructure considerations/build took place along with pharmacist-driven algorithm write-up. During this GPI, we’d like to discuss specific steps to make this happen along with sensible benefits we realized from implementing each technology.
What has been achieved?
Our hospital pharmacists got significantly more involved in direct patient care where notable efficiencies were realized on the operational side. In addition, medication education was significantly enhanced with improved patient access to their in-house hospital pharmacist.
What next?
Next steps include deploying these these technologies to further service lines and patient care areas, as well as investing into further meaningful technologies. We’ll review what’s in the pipeline as well.
Surveillance system for adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Kornelia Chrapkova, Stanislav Gregor, Michal Hojny
Why was it done?
A passive surveillance system exists in our country, giving limited options for the reporting of adverse drug reactions (ADR) to our National Drug Agency (NDA). The current system does not consider different patient´s criteria such as, age, variety of disabilities and preferences and does not enable healthcare professionals to report ADR in an easily accessible and comprehensive way.
In addition, our aim was to provide support to patients during the pandemic lockdown when accessing their general practitioner was difficult.
What was done?
A surveillance system was created to encourage and facilitate the reporting of potential vaccine adverse events (VAE) after healthcare professionals and patients received a COVID -19 vaccine that was administered in our vaccination centre (VC).
How was it done?
Following patients receiving a COVID-19 vaccination they were sent a text message with an information that in case of VAE they could contact us via text message, email, fill an electronic questionnaire or call us.
We assembled a team of 10 pharmacists providing a non-stop service for reporting VAE. To ensure consistency in advice given to patients a manual was created for a management of the most common and likely VAE.
By liaising with the Information Technology Department, we created an electronic tool integrated into the hospital information system (HIS) for recording VAE. This enabled us to make a comprehensive report and sent it directly to the NDA. Consequently, an alert on each reported VAE after the first dose of vaccine was available for every clinician to maximise patient´s safety.
What has been achieved?
Between 4th January 2021 and 8th June 2021:
6 109 732 vaccines were administered throughout our country.
5402 (0,09%) VAE were reported to NDA.
43 409 vaccines were administered in our VC.
3 456 (7,96%) VAE were reported to our VC out of which 816 were rated as unexpected and 28 as serious.
What next?
Presenting of the results of the project will be used as a part of the education of healthcare professionals in our hospital. By this sharing of knowledge our aim is to enable and maximise patient’s safety and treatment. The integrated electronic tool for recording and reporting ADR will be also applied for all other medications

























