THE IMPACT OF A WARD SATELLITE PHARMACY ON CLINICAL PHARMACY SERVICES AND POTENTIAL COST BENEFIET (submitted in 2019)
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Thewodros Leka, iun Grayston, Mashal Kamran, Biljana Markovic
Why was it done?
The Carter report recommended that about 80% of hospital pharmacist time should be spent on the wards to provide clinical pharmacy services. However, in our hospital’s surgical specialty at the time of this report, it was found that only 33% of pharmacist’s time was spent on clinical pharmacy services. This had a negative impact on:
• rate of medication errors and near misses
• supply of critical medicines
• pharmacist participation in productive ward rounds
• timely discharge of patients home
What was done?
The Pharmacy department made a successful business case to the Hospital executives to open a Satellite pharmacy to serve 4 surgical wards. The proposal was to recruit a dedicated clinical pharmacist and Medicines Management Technician, and set-up a dispensing satellite pharmacy.
How was it done?
The business case indicated that if funded, the new satellite pharmacy team would: • improve clinical pharmacy key performance indicators • improve patient safety • deliver a potential cost benefit Funding limitation was an obstacle and we have to convince the board.
What has been achieved?
We achieved 60−90% improvement in the objectives set in the business case as illustrated in Table 1 and 2. The pharmacy team won the annual quality improvement award of 2018. Table 1: Clinical Pharmacy Service improvement Clinical pharmacy services Service rate pre-satellite pharmacy Service rate post satellite pharmacy % of service improvement Medication errors 16/month 6/month 63% Pharmacist interventions 20/month 80/month 75% Pharmacist participation in ward round 6/month 50/month 88% Time to dispense discharge summaries 90 minutes/discharge summary 20 minutes/discharge summary 77% Number of patients counselled 15/month 75/month 80% Pharmacist available in the ward 1.5 hrs/day 7.5 hrs/day 80% Time taken to supply critical medicines 1 hour 5 minutes 91% Table 2: Potential Cost-benefit savings achieved Activities Cost-benefit savings/year (€) Reducing length of stay of patients €17,000 Reducing repeat dispensing €16,000 Effective use of nursing time €11,000 Reducing prescribing errors €103,000 Total Savings €147,000.
What next?
• Weekend working.
• Service improvements can be transferred to acute medical units and downstream medical wards. Reference Carter report.
THE RISK MANAGEMENT OF THE PHARMACY PREPARATIONS IN THE HOSPITAL PHARMACIES (submitted in 2019)
Pdf

European Statement
Production and Compounding
Author(s)
ADRIANA DURCANSKA
Why was it done?
The quality and safety standards of pharmacy preparations are not harmonised throughout Europe. They fall under the national competencies of individual European countries.
What was done?
The quantitative risk assessment of the pharmacy preparations for stock in hospital pharmacies (HPs) in accordance with Resolution EDQM CM / Res (2016) 1; to specify the decision criteria for the risk assessment; the risk management of the pharmacy preparations for stock in the country; to design a check list of the risk assessment for extempore preparations.
How was it done?
Out of the total number of 53 hospital pharmacies contacted, 5 pharmacies sent a suitable file.
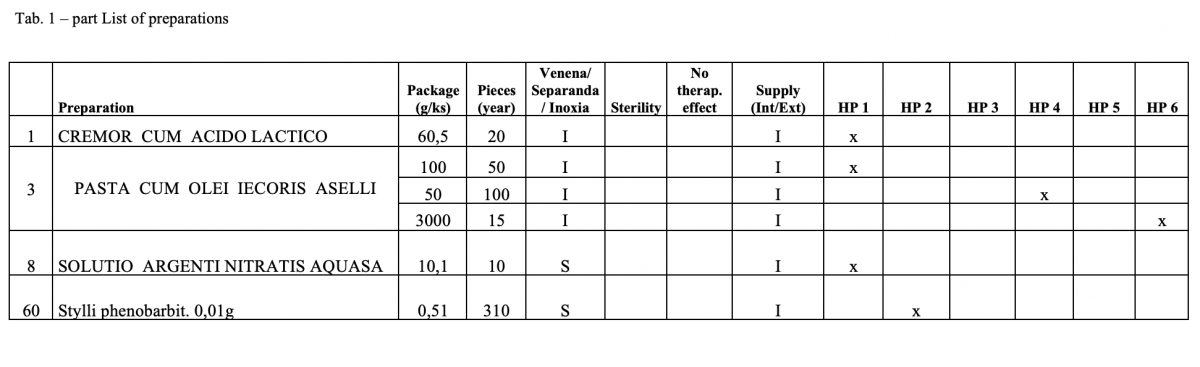
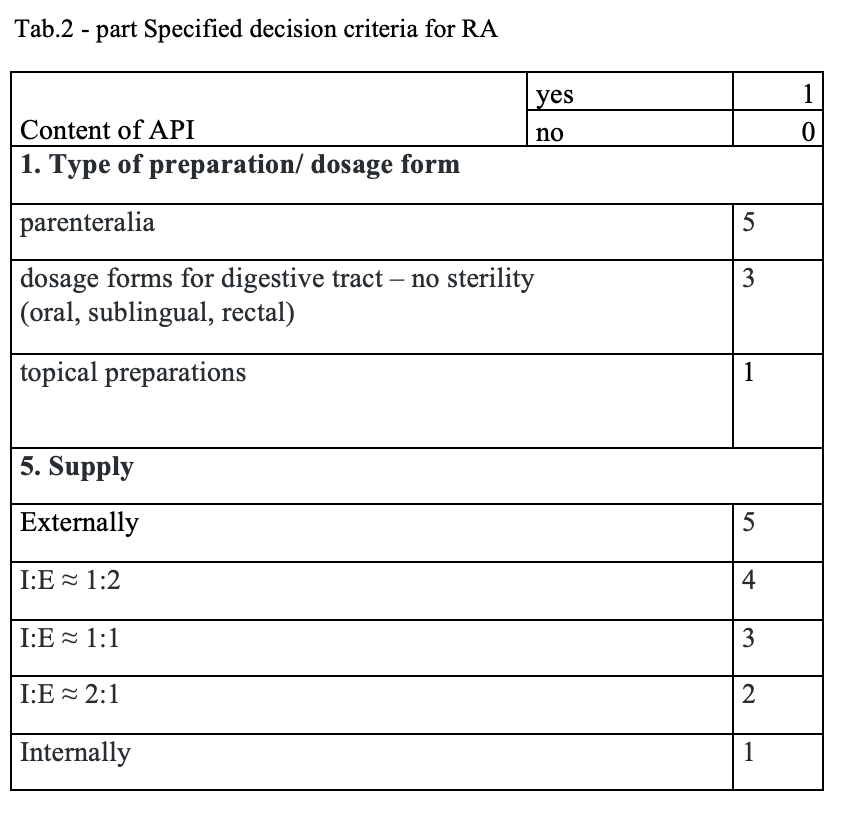
What has been achieved?
A total of 170 types of medicines are being prepared in HPs. One HP had the result of the risk ≥ 100 when preparing ophthalmic medicines. Annex A is a check list designed to assess the risk of extempore preparations.
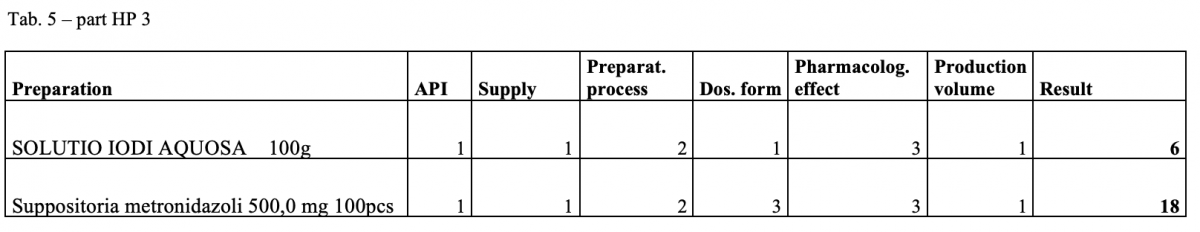
What next?
The management is and will be forced to consider its introduction or to use another model: hospital – GMP / outsourcing / central pharmacy preparing and distributing. The aim of using the document in hospital pharmacies of the country.
IMPLEMENTATION OF A MEDICATION SAFETY AGENDA AT TWO HOSPITAL SITES IN RESPONSE TO WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION (WHO) PATIENT SAFETY CHALLENGE ‘MEDICATION WITHOUT HARM’ (submitted in 2019)
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Meenal Patel, Sheena Patel, Peta Longstaff
Why was it done?
• Initiative introduced and on-going since 2017
• To increase and embed medication safety awareness
• To address under-reporting of medication-related incidents, with feedback
• To embed medication safety in education programmes and clinical practice
What was done?
A local medication safety agenda implemented across two hospital sites in response to World Health Organisation (WHO) patient safety challenge ‘Medication without Harm’.
How was it done?
• Medication safety group (MSG) introduced with local strategy, involving junior medical staff for frontline feedback • Medication safety metrics changed to allow benchmarking with peers as per NHS Improvement’s Model Hospital data • ‘Plan, Do, Study, Act’ model applied to improve transfer of care from hospital to rehabilitation unit following external incidents • Monthly analysis of incidents with harm, exploring reasons for under-reporting • Optimisation of incident reporting system to improve staff feedback following investigations • Near miss error log introduced in pharmacy with shared learning • Mitigation of medication-related risks e.g. medications safe storage action plan • Medication safety bulletins, patient safety newsletters and top tips guide introduced covering focal themes • ‘Safe prescribing’ mandatory induction training for junior doctors to support prescribing of high risk medicines and compliance to patient safety alerts • Hospital-wide education on lessons learnt from incidents • Medication safety resources for staff to access • Nursing quality round on medication safety • Electronic missed doses realtime report developed to tackle omitted/delayed critical medication doses • Medication safety awareness (MSA) week held to increase awareness on focal themes
What has been achieved?
• Multidisciplinary MSG with assurance on meeting WHO global challenge. • Monthly analysis of medication safety data to allow learning, collaboration and benchmarking against peers. • Positive staff feedback on bulletins/newsletters with staff involvement/engagement. • Training programmes embedded with safe prescribing education. • Improved hospital safety metrics: Following MSA week, a 5% and 21% increase in medication-related incident reporting occurred at each site which has been sustained. Reporting rates doubled at one site following success of MSA week. • In 2018-19, local target achieved for reported medication-related incidents per 100,000 finished consultant episodes and medication-related incidents with harm
What next?
• Collaborative multidisciplinary working raising the profile of pharmacists acting as medication safety officers
• Implementing medication safety measures from NHS Patient Safety Strategy 2019
• Initiatives for safer culture, safer systems and safer patients
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PREVENTION MEASURES FOR WOMEN IN PREGNANCY AND THE PUERPERIUM (submitted in 2019)
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Sheena Patel, Sima Purohit, Jennifer Hanna
Why was it done?
• VTE remains the leading cause of direct maternal death, with no evidence of a consistent decrease in mortality over the past 20 years.
• Alongside changes in national guidelines, the maternity population and interventions are changing e.g. women giving birth are now older with more risk factors for thrombosis e.g. obesity. More interventions e.g. caesarean section are undertaken placing women at higher risk of VTE.
• VTE prevention measures were introduced in 2010, and nearly 10 years on further changes were implemented to reduce mortality and morbidity.
What was done?
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) prevention measures introduced and embedded for women in pregnancy and the puerperium, with an aim to reduce potentially preventable hospital-associated events
How was it done?
• Electronic VTE risk assessment introduced with mandatory alerts at relevant time-points e.g. at booking, on admission, post-delivery • Simplification of the national VTE risk scoring system to ensure accurate completion of assessment and user-ability • Clear hospital guidance on VTE prevention for pregnant women, including a pocket guide covering risk assessment and thromboprophylaxis • Staff education on mechanical thromboprophylaxis for correct use and monitoring to avoid adverse effects • VTE patient information leaflet covering signs and symptoms of VTE and when to seek urgent medical attention • Introduction of a ‘mum and baby’ app with information during pregnancy and postpartum • Root cause analysis performed on hospital associated VTE events, with shared learning of root causes and actions to prevent recurrence to multidisciplinary teams • VTE education introduced in medical, midwifery and pharmacy staff training programmes, with regular updates in the maternity risk newsletter
What has been achieved?
• Over 95% of women with VTE risk assessments on admission, with weekly and monthly performance reports for local monitoring • Pharmacy staff perform quarterly audits on appropriate thromboprophylaxis. 97% inpatients received pharmacological thromboprophylaxis, and 88% inpatients were wearing anti-embolism stockings • Pre-printed VTE management plan in maternity documentation to assist with transfer of care • Development of an ‘app’ to provide patient information • Patients counselled on anticoagulant therapy to support medication compliance • VTE education embedded in training programmes • VTE ward rounds for ongoing stewardship
What next?
• Staff engagement to embed VTE prevention measures in practice
• Increasing patient education on VTE prevention
• Robust and sustainable interventions improving patient outcomes
THE IMPACT OF AN ELECTRONIC ALERT IN PREVENTING DUPLICATE ANTICOAGULANT PRESCRIBING (submitted in 2019)
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Alison Brown, Gillian Cavell, Nikita Dogra, Cate Whittlesea
Why was it done?
Anticoagulants are high-risk drugs. An NHS England Patient Safety Alert was published in 2015 highlighting harm from inappropriate co-prescription of anticoagulants1.
What was done?
A ‘duplicate anticoagulant alert’ (Anticoagulant MLM) was implemented within our electronic prescribing system (EPMA) to alert prescribers if co-prescription of two or more anticoagulants was attempted, with the intention of preventing the completion of a potentially harmful prescription. We conducted a retrospective review of the impact of the Anticoagulant MLM on preventing co-prescription of low-molecular weight heparin (LMWH) and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACS)
How was it done?
The study took place in a 950 bed UK acute teaching hospital. A report of all Anticoagulant MLM alerts generated for adult inpatients between 26th June 2017 and 8th October 2018 was extracted from EPMA. Data on drugs prescribed, alert acceptance or override and duplicate anticoagulant administration were collected. Where alerts were overridden, appropriateness of the override was assessed by an anticoagulation specialist pharmacist. Ethics approval was not needed.
What has been achieved?
The Anticoagulant MLM triggered on 894 occasions; 113 in response to attempted prescription of a LMWH for a patient already prescribed a DOAC. 65 of 113 alerts were overridden (duplicate prescription completed). 48 alerts were accepted (duplicate prescription avoided). Of the 65 overridden alerts, consecutive doses of both anticoagulants were scheduled appropriately. No duplicate doses were administered in 44 cases (44/65, 67.7%). 15 duplicate prescriptions were either cancelled before administration or not administered concurrently (15/65, 23.1%). Duplicate doses were administered against 6 prescriptions (6/65, 9.2%), on 3 occasions. No patient harm was identified. The alert prevented inappropriate co-prescription of anticoagulants to 48 patients. Overrides were justified in 44 cases. Anticoagulants were correctly prescribed for 92/113 (81.4%) patients. It was outside the scope of this project to investigate why alerts were overridden. ‘Alert fatigue’2 and alert frequency3 are recognised factors limiting the effectiveness of electronic alerts in changing a planned course of action.
What next?
The alert remains in place as a barrier to error. Further work is needed to identify reasons for anticoagulant alert overrides.
PARENTERAL NUTRITION: HOW TO PREVENT THE NEXT MISTAKE? (submitted in 2019)
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Why was it done?
In Carmel Medical Center, the infusion pack is delivered by a pharmacist according to the prescription given from PN staff, and afterwards the infusion instructions are recorded by one of the department physicians in the patient EHR. Recently there have been several mistakes that have been reported, which made it urgent to check matching between PN staff decision and the record of instructions in the EHR.
What was done?
Recognise the mismatch between the electronic health record (EHR) instructions for delivery of parenteral nutrition (PN), against the actual delivery by the pharmacy according to prescription from PN staff and characterisation of these cases in terms of mismatching.
How was it done?
Issuing a report of the PN doses delivered by the electronic system called “UNIT-DOSE” in the pharmacy according to the name of patient and days of treatment of 2018 vs. electronic instructions that have been recorded by one of the department physicians in the “Kamelyon” system or “Meta Vision ” The parameters examined were: type of solution, composition, volume, supplements-additives (electrolytes, vitamins, trace elements), infusion rate and method of infusion (central / peripheral). Infusion rate was examined separately as a follow-up by a nutritionist.
What has been achieved?
From our research, we found a significant difference between computerised recording of PN instructions and what the patient actually received. This is due to the separation between the hand-written prescription by the PN staff and the computerised instruction recording by the treatment team. This may constitute a danger to patients.
What next?
Examination and follow-up by the pharmacist is important for identifying and treating errors of this nature appropriately. Guidance sessions for the treating staff should be conducted in the different departments. The prescription must be matched by the PN staff to the computerised instruction by placing a prescription pattern. Set up protocols in the computerised system that guide the treatment staff in the department to record the correct instructions.
COMPENDIUM OF POST-GRADUATE ITALIAN HOSPITAL PHARMACY SCHOOLS: AN INFORMATIONAL GUIDE OF ReNaSFO ASSOCIATION – NATIONAL NETWORK OF ITALIAN HOSPITAL PHARMACY SCHOOL STUDENTS (submitted in 2019)
Pdf

European Statement
Education and Research
Author(s)
ANTONIO PIRRONE, FEDERICA MILANI, LUCA CANCANELLI, VALENTINA MARINI , DANIELE MENGATO , ROBERTO LANGELLA , NICOLA REALDON
Why was it done?
On October 5, 2017 the National Network of Italian Hospital Pharmacy School Students (ReNaSFO) was born with the aim to face the various critical aspects of post-graduate Hospital Pharmacy School (SHP), such as the need to make the different paths homogenous among regional SHPs, improve dialogue between colleagues and encourage a more informed approach focused to the training pathway for specialisation. In particular, little official information is available and hard to find about the different realities present in Italy.
What was done?
“Compendium” project is designed to fill this lack and to gather information on post-graduate SHPs operating in Italy. In addition to outlining a summary description of the SHPs, the Compendium is configured as an official tool to respond and provide targeted information to near-graduates and graduates in Pharmacy (who often contact ReNaSFO) interested to approach the SHPs path.
How was it done?
Two project coordinators prepared a list of items submitted to representative ReNaSFO student in every 21 operating SHPs. The items refer to: available places and admission requirements, type of entry test, organisation of didactic lessons, exams and residency training, health facilities affiliated with SHP, potential availability of scholarships, useful links of the SHP or university. The help of universities was fundamental, in particular the helpfulness of SHP directors to collaborate with students.
What has been achieved?
As many as 18 SHPs out of 21 (85.71%) have joined the project: Bari, Bologna, Catania, Catanzaro, Camerino, Genoa, Florence, Milan, Modena and Reggio Emilia, Messina, Naples, Padua, Parma, Pisa, Rome, Siena, Turin and Sassari; of these, 14 schools have already sent their finished “Compendium” form.
What next?
Thanks to the widespread presence of associated ReNaSFO students, the initiative has immediately found interest and participation, reconfirming once again the active and unconditional collaboration between SHP students throughout Italy. Despite a heterogeneous situation between different SHPs, we keep working together hopeful to achieve national uniformity of SHPs and to improve educational objectives and training pathways.
PROMOTING THE USE OF SAFER INJECTABLE MEDICINES USING A NOVEL METRIC
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Why was it done?
Despite the availability of RTU and RTA formulations of high-risk injectable medicines they were not always used. We developed the metric, to compare the use of RTU and RTA injectable medicines with the use of concentrates requiring further dilution or manipulation prior to administration e.g. dilution of morphine 10 mg/ml to 10 mg/10 ml prior to intravenous administration, e.g. withdrawal of 5 x 10 ml fentanyl 500 mcg/10 ml into a 50 ml syringe for continuous infusion, and identify areas for improvement.
What was done?
We have developed a series of metrics to measure compliance with national guidance for the safe use of injectable medicines. The guidance recommends use of ready-to-use (RTU) or ready-to-administer (RTA) injectable products, where these are available, to reduce the risk of patient harm from errors in the preparation of injections and infusions on hospital wards.
How was it done?
The metric utilises pharmacy-issue data to compare the number of units of RTU or RTA formulations issued to wards and clinical areas with the numbers of units of alternative products of the same drug entity. Expressed as a percentage the metric informs the organisation of the extent to which safer injectable medicines are being used, providing a baseline against which to review practice and reinforce the need to use alternative, safer formulations. A high percentage indicates good compliance.
What has been achieved?
The metrics have been used to successfully maximise the use of a range of safer formulations including RTA potassium chloride, RTU fentanyl 2500 mcg/50 ml vials for critical care infusion, 100 mg/10 ml paracetamol in neonatal units and RTU magnesium sulphate 20% (50 ml vials) for obstetric emergencies. Since the introduction of the metrics in 2016 a monthly scorecard of performance is reviewed by the Hospital Medication Safety Committee to identify and account for deviations.
What next?
The metrics are being shared with other organisations to benchmark performance. Ideas to promote implementation and business cases can be shared between organisations who may find implementing RTA and RTU injectable medicines challenging, especially where these are more expensive than formulations in established use.
IMPLEMENTING THE PRODUCTION OF STERILISED SYRINGES IN THE HOSPITAL: IMPROVING MEDICATION SAFETY AND SAVING HEALTHCARE COSTS
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Karin Larmene-Beld, Rommert Wijnsma, Gerrit de Weerd, Maarten Postma, Erik Frijlink, Katja Taxis
Why was it done?
Medication administration errors are common in hospital practice. Meta-analyses suggest that about 10% of administrations are erroneous, with much higher error rates occurring during intravenous drug administrations. It has been demonstrated that 21% of the errors can be eliminated when prepared syringes are used. Many countries struggle with the problem of optimising the process of safe parenteral medication in hospitals. Different guidelines across countries outline how preparation of parenteral medication in the clinical environment should be done. Recently the Council of Europe published a resolution about preparation of medication which encourage the supply of ready-to-administer products by the pharmacy. Moving the activities of preparation of medication from the clinical environment to the pharmacy requires investments in pharmacy equipment but will result in efficacy, better quality and reduction in preparation medication errors in the hospital.
What was done?
Development and implementation of sterilisable plastic syringes produced in the hospital pharmacy for large-scale production of ready-to-administer products.
How was it done?
A new development in this area are ready-to-administer pre-filled sterilised syringes (PFSS) produced by the pharmacy. PFSS are produced on stock under GMP conditions by the hospital pharmacy using (semi) automatic filling and closing machines whereby quality and safety are embedded in the whole process of manufacturing. A total cost of ownership analysis is performed showing PFSS prepared in the hospital pharmacy yielded cost savings compared to conventional preparation on the ward. The process of production, filling, closing and sterilisation has been validated using newly acquired equipment. With the introduction of the cyclic olefin polymer (COP) syringes a new type of primary container is implemented in the pharmacy. To ensure patient safety and product quality a science- and risk-based strategy has been developed for testing extractables and leachables to qualify the new container as primary packaging material.
What has been achieved?
Introducing PFSS is cost saving for the healthcare system:– COP syringes are suitable as primary packaging material; –enhancement styles for better readability of labels are established; and – already, 15 products are validated and available for use in the hospital.
1. KHM Larmené-Beld KHM, Touwen-Spronk J, Luttjeboer J, et al. A cost minimization analysis of ready-to-administer pre-filled sterilized syringes in a Dutch hospital.. Submitted for publication in Clinical Therapeutics.
2. Larmené-Beld K, Kuiper A, van Berkel S, et al. A science- and risk-based strategy to qualify sterilized prefilled syringes as primary packaging material in a hospital pharmacy. Abstract submitted for 24th EAHP Congress.
3. Larmené-Beld KHM, Kim Alting E, Taxis K. A systematic literature review on strategies to avoid look-alike errors of labels. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2018 74:985–93.
What next?
Introducing more drugs as ready-to-administer products. Optimising the label of ready-to-administer syringes to avoid look-alike errors based on the results of the review.
PROTOCOL IMPLEMENTATION FOR PRESCRIBING AND DISPENSING POSTEXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS KITS FOR HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS IN A THIRD-LEVEL HOSPITAL
Pdf

European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Clara Estaún-Martínez, Isabel Moya-Carmona, Laila Dani-Ben Abdel-lah, Jose Manuel Fernández-Ovies
Why was it done?
This initiative was taken in order to improve uptake and completion rates of PEP, and to homogenise the healthcare circuit for these patients and the prescribed drugs.
What was done?
A protocol was implemented in order to standardise the prescription and dispensation of postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) after occupational or nonoccupational exposure to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
How was it done?
A multidisciplinary team including Infectious Diseases and Preventive Medicine (PM) doctors, pharmacists and Emergency Room (ER) staff developed the following protocol for PEP according to World Health Organisation and national guidelines: – standard three-drug regimen for PEP: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/Emtricitabine + Raltegravir for 28 days. The pharmacy service (PS) repackages kits for five, 23 or 28 days that include antiretroviral drugs (AD) and written information about the treatment (use, length of the treatment, main interactions and side effects, contact number). Only 5-day PEP kits will be located in the ER. – Twenty-four-hour access granted to PEP kits as it is strongly recommended to initiate PEP as early as possible (ideally within 72h). –
Established healthcare circuit for patients in the ER:
• Monday–Fridays (8h00–15h00): patients will be immediately referred to PM, then they will go the PS in order to receive a 28-day PEP kit and pharmaceutical care.
• Out of this schedule and bank holidays: ER doctors will give patients a 5-day PEP kit and they will be referred to PM the next working day. After visiting PM, the patient will go to the PS in order to receive the rest of PEP (23-day kit) and pharmaceutical care. –
Several meetings took place in order to explain this new circuit to the health professionals involved and written copies were available on the ER as well as on the intranet.
What has been achieved?
The implementation of this protocol was well embraced by all the staff involved, since it allowed a more efficient healthcare circuit for the patients. It also optimises the evaluation and monitoring of these patients by PM and the pharmacist, and grants prompt PEP initiation and 24h access to the AD. The 28 days (or 5+23 days) kits help to accomplish the proper length of treatment, without using the regular packages which include 30 days of treatment (saving €43.17 per treatment).
What next?
We will monitor the compliance with this protocol and the drugs prescribed for PEP.


























