Disposable Closed System for Sterile Drug Preparation and administration
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Why was it done?
Our proposed system comes from the idea of a large clean room with pressure regimes, and airlock, hoods and other ancillary equipment, Which we made from it a very small clean room that is our box, when there will be no need for us as operators to get into it, or very simply take only those parts that are supposed to be sterile, and only those parts that are the two ends of the infusion bag and the end of the medicine vial
What was done?
“Closed” and airtight system for preparation (reconstitution, measurement, dilution) and injection of IV drugs at the patient’s bedside, in the various clinics and further home treatment, Disposable system, All its parts come in one piece without the need for threading, or assembly and disassembly
Estimated dimensions: 10 cm length, 5 cm width and 3.5 cm depth or similar, its shape can be rectangular or any shape convenient for use operation storage and destruction at the end of the process
Intended for a wide range of types of drugs – such as intravenous antibiotics, cytotoxic drugs, biological drugs, etc.
Designed according to its different variations for different types of vials and different amounts of drugs that come as a dry powder for dissolution, and are also suitable for drugs that come in the dissolved liquid form.
It is also intended for use with glass ampoules and there is a wide range of drugs that still come in glass ampoules
Intended for administration of drugs that do not need to be diluted in an infusion bag given in IV PUSH
How was it done?
We designed the device with 3D software (solid wark). It consists of a number of functional parts,
The sterile closed system comprises an airtight enclosure, which is shaped so as to define an enclosure interior; and an infusion-bag receptacle. An infusion-bag seal is configured, when in a sealing state, to make an airtight seal with respective external surfaces of a medication port and an IV tubing port of a bottom region of the infusion bag, when the medication port and an IV tubing port are inserted into the infusion-bag receptacle.
What has been achieved?
The proposed solution and its advantage
– A single-use system built in one piece, without the need for assemblies, disassembles, etc.
It will be possible to perform the entire process in one place, such as at the patient’s bedside or in the clinic, starting with the powdered drug dissolving process, mixing a measured dose, mixing it in an infusion bag and injecting it into the patient’s vein safely and accurately.
Maintains the perfect process under sterile conditions without fear of contamination of the injected drug
– Preparation in a system that is safe for the immediate environment and safe for the caregiver himself from contamination of drugs such as cytotoxic drugs, antibiotics and more
Savings in building very expensive infrastructure of clean rooms
Saving on very expensive disposables, such as closed system transfered deviced, robes and more
Save valuable work time dedicated team of pharmacists, nurses work time, work time transportation, storage places and more
Minimize the chance of errors in administering medications and confusion between different medications
Working with non-exposed needles reduces the chance of needle prick injury
What next?
Applied research will be carried out by pharmacists and nurses, in order to test the efficacy and safety of the device (by using a basic prototype), these experiments will use different IV administration drugs, we will test the method of dilution from a drug vials and glass ampoules, measure the exact dose and transfer to the infusion bag, and remove through the IV line, the accuracy of the preparation, the sterility of the preparation, the quality in terms of leakage or drip, comfort, safety and more are measured.
New frontiers of hospital pharmacy: management and preparation of human tissues used in the surgery room
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Andrea Ossato, Giuseppe Giovagnoni, Michele Giannini, Anna Francesca Spada, Francesca Realdon, Valeria Mezzadrelli, Lorenza Cipriano, Nicola Realdon, Teresa Zuppini, Roberto Tessari
Why was it done?
Since 1st October 2019, the regional tissue bank that supplies hospital, stopped sending ready-made tissue to the implant, preferring the shipment of tissues frozen at -80°C. For this reason, the hospital pharmacy developed a procedure for the management of orthopedic allografts ensuring a clear and safe supply chain reducing the waste raised from the obligation of immediate use of the thawed tissue.
What was done?
Hospital pharmacists, in agreement with the hospital administrators and the orthopedic surgery department, developed a new service characterized by procurement, processing, preservation, storage, thawing and preparation of human tissues and cells for orthopedic allografts, according to European and national legislation.
How was it done?
The management of orthopedic allografts took place as follows: was established a dedicated path for communications with orthopedic surgery and bank tissue; tissue thawing and washing was centralized in the clean-room of the hospital pharmacy and were guarantee adequate training of all personnel involved as well as complete standard operating procedure documentation for all stages of the process and appropriate control measures.
What has been achieved?
Evaluation of the process showed that it was favourable in terms of practicality, safety, traceability and cost saving. Especially, the centralization of tissue preparation within clean‐rooms with aseptic technique, allows microbiologically safer setups reducing clinical risk. A further guarantee of safety is given by the sterility process’s validation through Media Fill test. This organisation allowed us to reduce the waste through a more effectively management of the tissues shelf life and any missed surgery with a cost saving and an ethical behaviour.
What next?
Optimise patient outcomes through working collaboratively within multidisciplinary teams and using the limited health systems resources responsibly, are two main goals expressed by the last European Statements of Hospital Pharmacy (ESHP). This study demonstrated how the centralization of tissues management in the hospital pharmacy make the process more efficient and safer and thus comply with the ESHP’s goals; leading to a clinical advantage for patients and better economic impact for the hospital.
A new vancomycin formulation for oral use
European Statement
Production and Compounding
Author(s)
Mette Lethan, Tove Hansen, Trine Schnor, Louise Rasmussen Duckert
Why was it done?
Oral vancomycin 125 mg four times a day for 10 days, is the common treatment for antibiotic-associated clostridium difficile colitis. As solid oral formulations are unsuitable due to strong diarrhea, an i.v. formulation in a diluted form (10 mg/ml) is used. However, several issues with that use, required the need for creating a new formulation.
The product is used for treatment of kids and adults, often with nausea. The low strength requires large volumes of solution and with no flavoring the liquid is very bitter.
Furthermore, the current solution has a limited stability causing difficulties as it is often desired to treat the patients at home. Therefore, a wish arose for a new formulation with a higher concentration, better stability and improved organoleptic qualities.
What was done?
A new oral formulation of Vancomycin was developed to improve the treatment of antibiotic-associated clostridium difficile colitis. The new formulation consists of the active ingredient (API) Vancomycin as a powder with a solvency for dissolving prior to use.
How was it done?
To obtain the best stability it was selected to make a new formulation consisting of a premeasured API, with a solvency ready to mix before use, to obtain a final strength of 50 mg/ml and a volume equivalent to 48 hours of doses.
Vancomycin in pharmacopeia quality was acquired and analyzed. A solvency was formulated mostly consisting of water, conservation and orange flavoring. A test was conducted with a weighed-out API to ensure that it was dissolvable with the solvency in the selected packaging.
What has been achieved?
A product achieving the wanted changes was tested and made. Making a formulation consisting of a premeasured powder creates the possibility of a higher durability. When mixed with the flavored solvency, the wanted strength is achieved.
The new formulation can be stored at room temperature before dissolving. It can be dissolved by the patient before use and kept refrigerated until the full volume is used. The product is easy for the patient to handle and therefore enables treatment in the patients own home.
What next?
A new product was made. Final use by patients will be tested for ease of use and potential home treatment.
OPTIMIZATION AND CENTRALIZATION OF THE HANDLING CIRCUIT OF HAZARD DRUGS FROM THE PHARMACY SERVICE
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Mireia Iglesias Rodrigo, Júlia Pardo Pastor, Alba Manzaneque Gordon, Cristina Sangrador Pelluz, Núria Meca Casasnovas, Clara Sebastián Carrasco, Fernando Salazar Gonzalez, Gemma Garreta Fontelles, Jordi Nicolás Picó
Why was it done?
Due to the risk posed by the handling of Hazard Drugs (HD) in the healthcare field, it is necessary to implement circuits that guarantee the professional’s safety.
What was done?
Create an internal classification of HD based on the NIOSH List of Hazard Drugs in Healthcare Setting 2020, to optimize the circuit of its handling from its receiving to its administration.
How was it done?
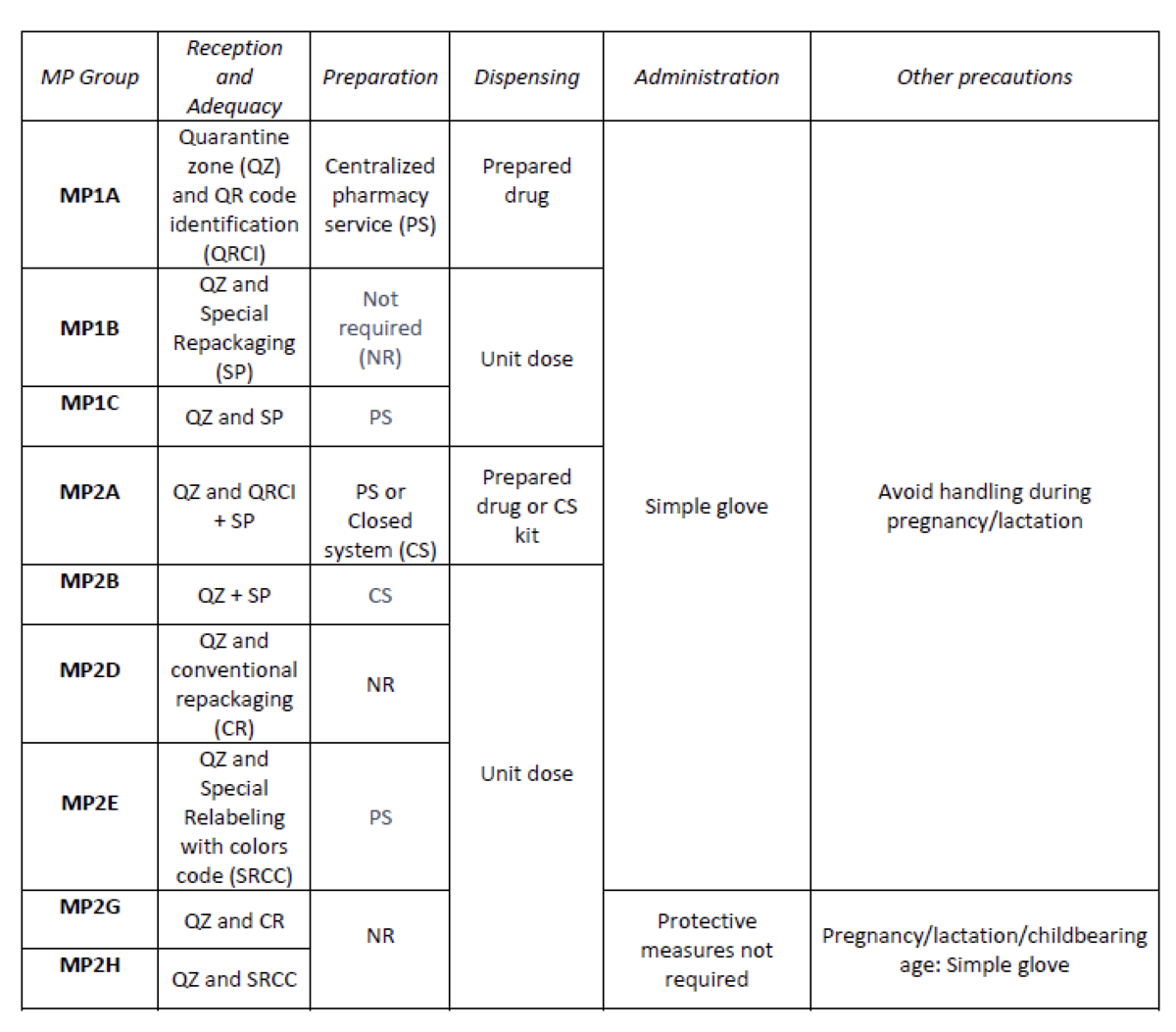
Considering the HD included in the Pharmacotherapeutic Guide (PTG) of our center, the stages of reception and adaptation/preparation/dispensing/administration and other precautions were analyzed.
Categories were established, analyzing the needs of each stage according to: NIOSH level of danger, setting (inpatient/outpatient), pharmaceutical form, commercialized pharmaceutical specialties or available alternatives, and material/personal resources.
Prior to its implementation, e-learning training was carried out for the healthcare professional involved.
What has been achieved?
A total of 25.3% (379/1498) of the pharmaceutical specialties included in PTG were HD. Thirteen HD groups were identified. Due to the fact that in the outpatient setting the drug is dispensed to the patient in its original container, the actions implemented were only carried out for inpatients, representing these 9/13 of described groups. The established training was carried out by the 89% of professionals. Proposed measures for HD are summarized in Table 1.
What next?
Monitoring and evaluation of the circuit
Compounding an extemporaneous sterile antibiotic solution for treating an infected wound
European Statement
Production and Compounding
Why was it done?
To solve a problem with a foot wound of a young man not responding on the standard secondary surgical healing intention wound treatments, that appeared at the General surgery department of our hospital.The wound was infected with 2 bacteria, S. aureus and Enterococcus species.The patient was quite long time treated with i.v. antibiotics without result.The wound infections are one of the biggest common nosocomial problems that demand special professional team engagement.
What was done?
Compounded an extemporaneous sterile vancomycine and gentamycine solution for secondary healing intention wound treatment.
How was it done?
A responsible pharmacist being alone on an afternoon duty, initiated a topical application of sterile antibiotic solution according to wound’s antibiogram.The surgeon demonstrate suspicion due to lack of that kind of experience/practice.So 100 ml solution was prepared under sterile conditions of the Department for infusion solutions production in our hospital, containing 50 mg/ml vancomycine and 1.2 mg/ml gentamycin in a 0.9% sodium chloride sterile and nonpyrogenic solution for i.v. administration.According to the SmPCs of the antibiotics manufacturers we determined 7 days expire after production, kept on room temperature.
What has been achieved?
A departmental surgeon has accepted the initiative and treated the wound twice daily at the surgery department.On the second day of applying, the wound edges held closely together and the wound has started epithelialisation.There were not any allergic reactions, significant tingling, itching and pain on the skin around the wound.On the third afternoon of introducing the solution use, the patient was discharged home and reassigned for an ambulatory treatment i.e. daily hospital, for once daily wound washing with the sterile solution.We prepared the second dose of the solution on the 7th treatment day and the wound was healed on the 13th day.
What next?
To incorporate this GPI into daily surgical standard procedures for bacterially infected wounds for a best patient issues.
Semi-automatic COVID-19 vaccine preparation for upscaling of vaccination
European Statement
Production and Compounding
Author(s)
Denise van der Nat, Anouk Lindemans, Laurens van Rijn, Wilfred Weijers, Elisabeth Ruijgrok
Why was it done?
COVID-19 is an ongoing worldwide pandemic which causes millions of deaths. To reduce COVID-19 mortality and morbidity, vaccines are developed. However, preparing COVID-19 vaccines before administration is a time consuming process. To accelerate this process and increase efficacy for health care workers, the Vaxtractor was designed in January 2021. We aimed to examine the quality of COVID-19 vaccines prepared with the Vaxtractor.
What was done?
Development and testing of a device (Vaxtractor) for semi-automatic large-scale preparation of COVID-19 vaccines.
How was it done?
With the Vaxtractor, the desired volume of vaccine is drawn up automatically in syringes from two vials of vaccine simultaneously. A sterility test, measurement of accuracy and uniformity of dosage units tests were performed in September and October 2021. For the sterility test, 22 syringes were filled with 0.5 ml Tryptic Soy Broth and these were incubated at 25°C for seven days followed by a seven day incubation period at 30°C. For the accuracy and uniformity of dosage units test, 60 syringes were filled with vaccine. Subsequently, the filled and emptied syringes were weighed. Furthermore, a time analysis was performed on manually and semi-automatically prepared COVID-19 vaccines.
What has been achieved?
The sterility test showed no visual sign of growth of micro-organisms. Furthermore, the weight of 60 prepared Spikevax® vaccines deviated less than 5% compared to the average weight of the vaccines. Also, the observed volume per vaccine deviated less than 5% compared to the declared volume. Besides that, preparing COVID-19 vaccines with the Vaxtractor was about three times faster compared to manually prepared vaccines and reduced the risk of needlestick injuries.
What next?
The Vaxtractor can be used to safely prepare Spikevax® vaccines. In the next months we will assess the quality of preparing Comirnaty® vaccines with the Vaxtractor. If these results are positive, the device can be implemented at large scale at the in- and out-of-hospital setting. This will contribute to effective upscaling of COVID-19 vaccination.
Design and implementation of a course on “Improving the understanding of biosimilar formulation science through Real-World Training”
European Statement
Education and Research
Author(s)
Paola Minghetti, Giuseppe Danilo Norata, Francesca Selmin, Paolo Rocco, Vito Ladisa, Margherita Galassi
Why was it done?
The availability of mAbs to treat different pathologies is steadily growing, causing a steep increase in the level of training needed in different areas of pharmacists’ intervention, including compounding, handling and storage. As this process will be sustained by the increasing availability of biosimilars, pharmacists, the key health professionals responsible for their compounding and handling, will face new challenges.
The aim of this project is to overcome the common problems encountered by hospital pharmacists in obtaining education on biosimilars, included limited financial support, heavy workload or inadequate educational resources.
What was done?
A self-paced educational course has been designed and implemented with the aim of providing a fundamental grounding in the physical chemistry, pharmacology and technology of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)-based medicines in oncology, both originators and biosimilars and the methodology associated with their compounding and handling.
The primary target audience for this project consists of hospital pharmacists in the EU, though students in the specialization in Hospital Pharmacy and community pharmacists may benefit from the course.
How was it done?
The course has been designed and developed to address, previously assessed, unmet educational needs. The resulting format comprises both theoretical and remote real-world training on the pharmacology, technology and stability of mAbs, the technology and rationale of biosimilars and the regulatory aspects of biotechnological medicinal products.
What has been achieved?
A series of webinars in on demand movie format has been produced. The webinars contain a comprehensive theoretical section – covering biosimilar mAbs pharmacology and formulative and regulatory aspects – and a practice section in which the preparation steps of oncology mAbs are filmed and discussed in a hospital setting. All training activities have been recorded in remote both in Italian and in English. Every module is designed to be used as a single unit and has a duration of approximately 30 minutes. The total duration of the course is 8 hours.
What next?
The course will be CME accredited in Italy through Fondazione Francesco Cannavò, nonprofit CME provider of the Federation of Italian Pharmacists Associations. It will be made available to pharmacists through national and international CME platforms, providing fundamental grounding in the methodology associated with oncology monoclonal antibody biosimilar formulation.
IMPLEMENTATION OF AUTOMATED COMPOUNDING TECHNOLOGY IN A SPANISH HOSPITAL PHARMACY
European Statement
Production and Compounding
Author(s)
CARMEN MARÍA VALENCIA SOTO , ADELA GARCÍA-AVELLO FERNÁNDEZ-CUETO, SARA BARBADILLO VILLANUEVA, MARÍA OCHAGAVÍA SUFRATEGUI, MARÍA VICTORIA VILLACAÑAS PALOMARES, VIRGINIA MARTÍNEZ CALLEJO , MARÍA MARTÍN LÓPEZ, MARÍA RIOJA CARRERA, PAULA DEL RIO ORTEGA, MARTA VALERO DOMÍNGUEZ
Why was it done?
This project aimed to optimize security in the production workflow through automation of anti-cancer drugs compounding.
The use of recognition systems and gravimetric control guarantee traceability and accuracy in the compounding process, therefore improving patient safety.
Robotic systems avoid exposure to cytotoxic drugs, promoting healthcare operator safety. Moreover, once loaded, it runs automatically, liberating the operator for more complex preparations.
What was done?
In 2021, our hospital pharmacy implemented APOTECA platform, including management software (APOTECAmanager), two guided preparation systems for semiautomatic compounding (APOTECAps) and a robotic system for aseptic preparation of antineoplastic drugs (APOTECAchemo).
How was it done?
We configured each drug in the management software: dimensions, density, stability and expiration data, solvent, bags and transfer set information, QR code, etc.
A 3-phases process was scheduled:
– Integration between APOTECA and the hospital’s Electronic Prescribing Software (EPS). Carried out between November and December 2020.
– Training period: 8 weeks between May and July 2021, including pharmacists and technicians with progressively incorporation to real compounding.
– Real production analysis: 8 weeks between July-September 2021 (38 days, excluding weekends and bank holidays). Previously trained staff gradually trained the rest of the personnel.
What has been achieved?
During the 8 weeks considered, 4629 doses were elaborated, excluding clinical trials preparations.
APOTECA production supposed 85% (3944) of our daily compounding: 62,8% (2475) with the 2 semiautomatic systems and 37,2% (1469) with the robot. 99% of the doses prepared in APOTECAchemo were infusion bags and 1% syringes. In APOTECAps, 85% were infusion bags and 15% syringes.
Average dosage error for all preparations was 0,95% (±1,13) for APOTECAchemo and 1,57% (±1,31) for APOTECAps.
Up to data collection, 67 substances that fulfilled the criteria had been processed in APOTECA system and 41 of these in APOTECAchemo.
The top five ingredients compounded in APOTECA were: paclitaxel, carboplatin, pembrolizumab, etoposide and fuorouracil.
What next?
The implementation of this technology has improved patient and operator safety, as well as our daily workflow.
To ensure an optimal use we need to increase robot production by optimizing its operating hours and promoting more preparations in advance.
How to become a resilient chemotherapy preparation unit?
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Victorine MOUCHEL, Romy LINOSSIER, Chloé FERCOCQ, Jean-Luc PONS, Lucie BAILLET
Why was it done?
Injectable anti-cancer drugs are critical drugs and production disruption would result in discontinuity of care. Moreover, 60% of the production is dedicated to external clients as part of outsourcing contracts. To strengthen client’s confidence, we achieved the ISO 9001 certification in 2019. Implementing a BCMS is part of the overall quality and resilience process.
What was done?
In our hospital centre, production of injectable anti-cancer drugs is centralised in a chemotherapy preparation unit. Within the unit, we decided to implement a business continuity management system (BCMS). Therefore, we established and validated a business continuity plan (BCP) to face a production disruption and continue the delivery of products.
How was it done?
We followed the ISO 22301:2019 standard methodology. First, we performed the risk assessment as described by the ISO 22300: 2018 standard. A multidisciplinary working group (pharmacists, pharmacy technician, quality engineer) identified and analysed the risks likely to threaten the unit’s business continuity (BC). Risks were rated in term of criticality (Cr) from 1 to 4 and risks with Cr ≥ 3 were considered as priority risks. Then, a business impact analysis was led by the pharmacists and validated by the department chief. Strategies were set to face priority risks in accordance with the BC objectives. Finally, we documented the BCP and validated it thanks to tests followed by debriefing.
What has been achieved?
The risk assessment highlighted 23 risks and 13 of them (57%) were rated as priority risks. Most of the risks revolve around unavailability of production equipment or premises (fire, flood, natural disaster). The treatment of 7 of these risks was included in the action plan for 2021. Three strategies were documented to treat these risks: extended opening hours of the unit, closed system transfer device used in a contaminated isolator and production relocation in two other centres. Five tests were conducted to check necessary procedures and devices to use these strategies (closed system transfer device, remote access, transportation). Tests will be repeated yearly to maintain the BCP.
What next?
In conclusion, implementing a BCMS represents a continual improvement approach that will improve the unit’s ability to cope with a crisis in an appropriate way.
Development of method for mobile aseptic preparation of advanced therapy medical products
European Statement
Production and Compounding
Why was it done?
The pharmacy received a request for reconstitution of an ATMP Luxturna. The pharmacy or hospital did not have a suitable aseptic facility that could perform the reconstitution in a way that allowed the ATMP to be administered to patients before the expiry after reconstitution (max. 4 hours).
What was done?
Development of a single use isolator for advanced therapy medical products (ATMP) or gene therapy drug preparation was undertaken. The single use isolator had to be mobile to enable pharmacy staff to preform reconstitution directly on ward or in OP-theatre. It had to comply with Health and Safety regulations and at the same time make it possible for pharmacy staff to use aseptic technique to be able to reconstitute ATMP.
How was it done?
A review of isolator technology was performed, and a suitable solution identified. The set-up was further developed in a team with representatives from pharmacy, the eye department at Rigshospitalet-Glostrup. A manufacturer of the equipment was selected, and development performed. The set-up for ATMP preparation was presented to The Danish Health and Safety (DHS) department responsible for handling this type of treatment. The approval was granted after a standard 90-day period. Pharmacy staff were trained in working with the set-up and a dry run made in the eye theatre with the full surgical team.
What has been achieved?
10 patients (19 eyes) have been treated, 4 male and 6 female patients with age span 12-39 years. After having performed the procedure twice there was enough routine to treat 2 patients per theatre day hence reducing the cost of preparation and increasing efficiency of the team.
The pharmacy and surgical team have established a great working relationship and now consider the set-up as routine.
In spring 2021 the set-up was approved by (DHS) for reconstitution of Zolgensma. On July 1 a pediatric patient was treated with Zolgensma using the method.
What next?
Plan to develop the method further and make it available for coming preparations of ATMPs and share knowledge of the method with other hospital pharmacy organizations.
























