Initial observations on the implementation of a clinical pharmacy service in a rural hospital in Austria
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Sonja Guntschnig, Aaron Courtenay, Ahmed Abuelhana, Michael Scott
Why was it done?
The service was established as part of the implementation of a new pharmacy into the hospital. The aim of this good practice initiative was to introduce multidisciplinary work on the wards and provide clinical pharmacy support for the ward personnel. Furthermore, it determined what types of clinical pharmacy interventions are needed at a rural 360-bed hospital in Austria, and assessed the physicians’ acceptance rate of the pharmacists’ suggestions.
What was done?
A new clinical pharmacy service (CPS) was introduced into Tauernklinikum Zell am See.
How was it done?
Data on 550 interventions made by one clinical pharmacist were collected by convenience sampling over a one-year period and rated on a six-point clinical significance scale. A subset of 26 interventions was rated for clinical significance by four independent physicians to determine inter-rater reliability (IRR). A two-way model inter-rater reliability analysis was performed for the four different physician assessments using SPSS to determine intra-class correlation (ICC).
What has been achieved?
Prompt acceptance rate by the physicians involved was 71.3% (392/550). In 26.9% (148/550) of all cases, the physician considered a change. The overall average score for all 550 clinical pharmaceutical interventions taken was 2.2. ICC significance scores were correlated with the pharmacist’s scores, ICC for consistency was 0.732 and 0.732 for absolute agreement, thus both can be considered as “good”. Potential for cost reduction associated with the recommended pharmaceutical changes, namely with medication being stopped or dose reduction was 32.7% (180/550) and 25.1% (138/550), respectively.
What next?
There is great potential and a definite need for the expansion of CPS in Austria. Only 15.8% of Austrian hospitals have a pharmacy department with even less offering CPS. Many countries have demonstrated the benefits of CPS in hospitals over the past 30 and more years. The need for increased pharmacist staffing in Austrian hospitals needs to be demonstrated to Austrian stakeholders.
An interprofessional team for the management of nausea and vomiting in a haematological oncology unit
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Mapi Fleury, Januska De Maria-Lee, Alessandra Taiana, Yvan Bourgeois, Sophie Voruz, Olivier Spertini, Pierre-Yves Bochud
Why was it done?
In 2019, procedural changes within unit treating malignant haemopathies raised awareness about unsatisfactory management of NV, particularly CINV. We identified a lack of departmental consensus, leading to heterogeneous therapeutic practices, confusion over the aetiologies of NV and feelings of powerlessness among healthcare professionals. We decided to improve the whole process, from prophylaxis to treatment, by addressing specific knowledge gaps concerning CINV, improving pathophysiological and pharmacological knowledge, and implementing interprofessional management and MASCC/ESMO guidelines.
What was done?
Patient nausea and vomiting (NV)—particularly chemotherapy-induced NV (CINV) in malignant haemopathies—was managed by an interprofessional team.
How was it done?
A multidisciplinary working group was established to create a comprehensive, patient-centred NV management programme. Work sessions focussed on attaining a therapeutic consensus and adapting international guidelines to our context. Different professions learnt about each other’s needs and fields of competency, enabling each to be heard and creating mutual benefits through sharing expertise and knowledge. Pathophysiological/pharmacological leadership was given to clinical pharmacist, including developing and teaching specific protocols and supervising complex clinical situations in the field.
What has been achieved?
Interprofessional consensus was reached, documentation and techniques were implemented including clinical evaluation checklists at patient admission. CINV therapeutic regimens were completely updated and immediately and automatically included in cancer treatment protocols. The clinical pharmacist and specialist nurses give initial interprofessional training to new colleagues and ensure continuous on-site supervision. This transversal work has resulted in fewer patients suffering from NV and better team understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms, differential diagnoses and adverse drug effects—this also ended the use of unsuitable medications and dosages. Overcoming this critical situation also allowed us to begin non-pharmacological integrative care.
What next?
Interprofessional working group proved indispensable to this approach. Including CINV pharmacotherapy directly into cancer treatment plans is one of programme’s strong points and contributes to high adherence to guidelines. Team feels more relaxed and more in control. Monitoring is now done by tracking files and oral feedback, but we aim to implement systematic follow-up of interventions, care evaluations and NV to assess programme’s impact. Next stage will also include patient feedback.
OPTIMIZATION AND CENTRALIZATION OF THE HANDLING CIRCUIT OF HAZARD DRUGS FROM THE PHARMACY SERVICE
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Mireia Iglesias Rodrigo, Júlia Pardo Pastor, Alba Manzaneque Gordon, Cristina Sangrador Pelluz, Núria Meca Casasnovas, Clara Sebastián Carrasco, Fernando Salazar Gonzalez, Gemma Garreta Fontelles, Jordi Nicolás Picó
Why was it done?
Due to the risk posed by the handling of Hazard Drugs (HD) in the healthcare field, it is necessary to implement circuits that guarantee the professional’s safety.
What was done?
Create an internal classification of HD based on the NIOSH List of Hazard Drugs in Healthcare Setting 2020, to optimize the circuit of its handling from its receiving to its administration.
How was it done?
Considering the HD included in the Pharmacotherapeutic Guide (PTG) of our center, the stages of reception and adaptation/preparation/dispensing/administration and other precautions were analyzed.
Categories were established, analyzing the needs of each stage according to: NIOSH level of danger, setting (inpatient/outpatient), pharmaceutical form, commercialized pharmaceutical specialties or available alternatives, and material/personal resources.
Prior to its implementation, e-learning training was carried out for the healthcare professional involved.
What has been achieved?
A total of 25.3% (379/1498) of the pharmaceutical specialties included in PTG were HD. Thirteen HD groups were identified. Due to the fact that in the outpatient setting the drug is dispensed to the patient in its original container, the actions implemented were only carried out for inpatients, representing these 9/13 of described groups. The established training was carried out by the 89% of professionals. Proposed measures for HD are summarized in Table 1.
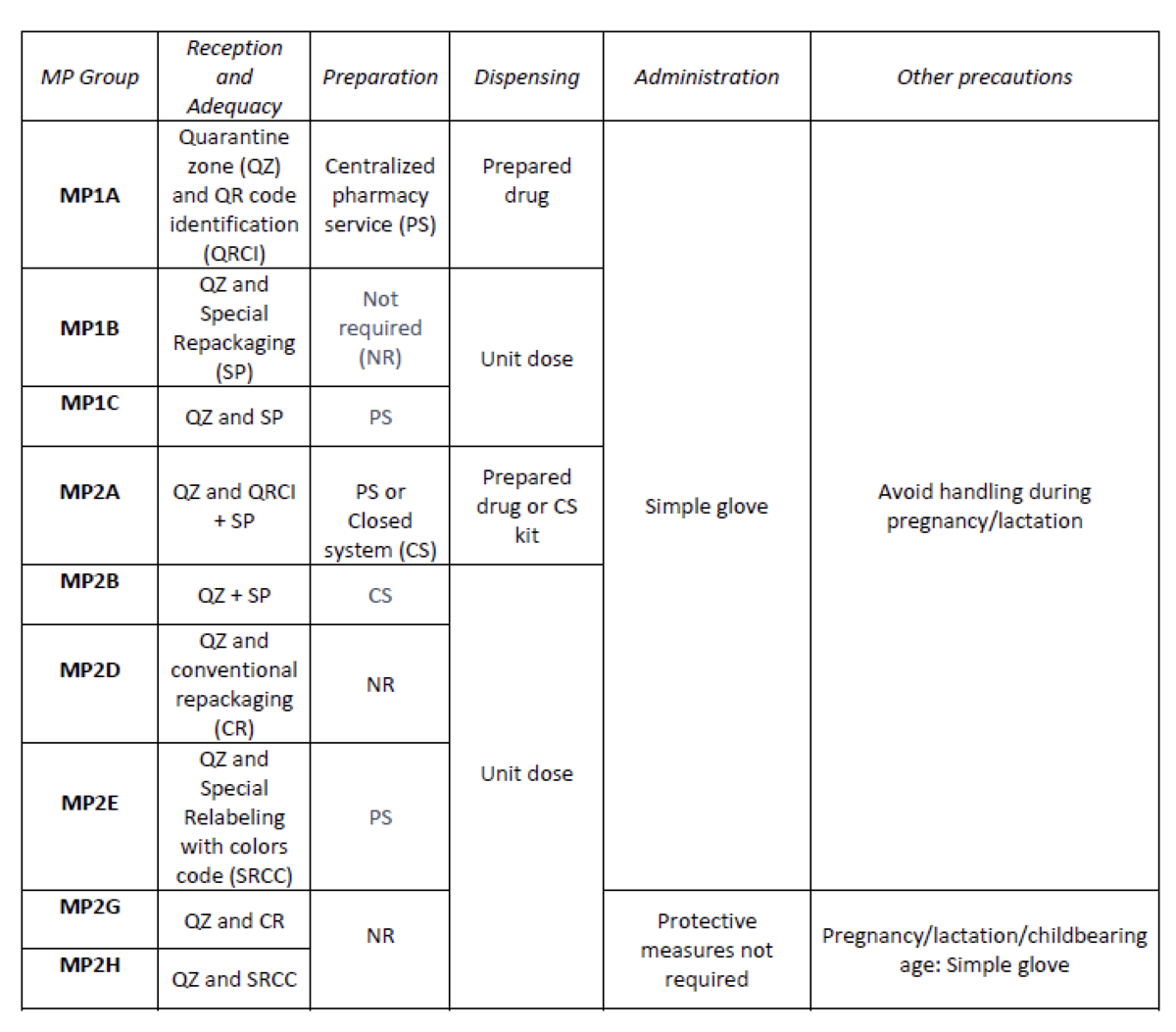
What next?
Monitoring and evaluation of the circuit
Optimizing information on the fecal microbiota transplantation circuit
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Julia Santucci, Céline Vaesken, Guillaume Saint-Lorant
Why was it done?
FMT is a therapy introduced in 2016 at the hospital. It is indicated for the management of recurrent and refractory Clostridioides difficile (CD) infections. In November 2020, with the resumption of the activity, we note a lack of knowledge of the different actors on this circuit: physician, nurses, fellows, patients himself.
The objective of the study is to reinforce the understanding and safety of the FMT circuit in a university hospital after the evaluation of the knowledge of the different actors.
What was done?
Implementation of a document to represent the circuit of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) in a French university hospital.
How was it done?
In this context, two questionnaires containing less than five questions on the functioning of the circuit were carried out with the nurse coordinators (NC) and the interns of the hepato-gastrology department. Subsequently, a document was drafted in consultation with the referring physician, the head of department and the pharmaceutical team to represent the FMT circuit.
What has been achieved?
With regard to the questionnaires, we obtained six answers from the NC, with 42% correct answers, 25% partial answers and 33% incorrect answers, and then six answers from the residents, with 20% correct answers, 7% partial answers and 77% incorrect answers.
These questions made it possible to draw up a diagram adapted to A4 format intended for all the actors in the circuit. It defines the different missions of all the actors with the corresponding deadlines and associated procedures.
In order to improve information, two interventions were carried out by the pharmacy: a staff meeting dedicated to the management of CD infections with the interns, co-hosted with the referring physician, and a presentation of the circuit to the NC.
What next?
Finally, this study made it possible to reinforce the safety of the FMT activity for the patient and to improve the management of the circuit for the various health professionals involved in this specialized therapy.
Implementation of a workshop about the role of the hospital pharmacist role during the clinical clerkship in medical training
European Statement
Education and Research
Author(s)
Vincent ARCANI, Stéphane HONORÉ, Guillaume HACHE
Why was it done?
Interprofessional collaboration as an effective means for improving healthcare outcomes. In order to achieve an effective level of collaborative healthcare practice, health care educators must focus attention on interprofessional education in undergraduate programs. Knowledge of professional role of others is a key competency for interprofessional practices and there is a lack of knowledge on hospital pharmacists’ roles among other health care professionals.
What was done?
We developed a workshop focused on the role of hospital pharmacists, to be integrated into the curricula of other health professionals.
How was it done?
The workshop was developed by a resident in hospital pharmacy and a senior hospital pharmacist, and we first targeted medical curriculum. The session integrated: students’ perception of hospital pharmacists’ role, didactic learning on the role of hospital pharmacists according to the European statements in hospital pharmacy, immersion in practice and evaluation. The assessment of the learning effect was performed by a pre-/post-workshop questionnaire, assessing satisfaction, metacognition and acquired knowledge. In addition, students provided open feedback on the workshop.
What has been achieved?
We implemented the workshop during the first year of clinical clerkship in medical education. Preliminary results highlighted (i) a high satisfaction, illustrating the relevance of the initiative; (ii) an increase in perceived knowledge and (iii) an increase in knowledge about hospital pharmacists’ roles, especially about pharmaceutical technologies and medical devices. Verbatim analysis of the feedback suggested that the workshop modified medical students’ perceptions on the role of hospital pharmacists, and that they may be more inclined to seek collaboration with hospital pharmacists.
What next?
To integrate the workshop into the curricula of the other professions in order to raise awareness on hospital pharmacy and promote interprofessional teamwork.
Improved drug management for surgical inpatients through the presence of a clinical pharmacist at the preoperative clinic
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Françoise LONGTON, Olivia Polinard, Linda Mattar, Anna Pauels, Mireille Bourton, Michel Mattens
Why was it done?
A thorough medication history at admission reduces medication errors. The presence of a clinical pharmacist in the preoperative clinic increases the number of inpatients who receive a standardized medication history by a pharmacist.
On admission, the adaptation of home medications to the hospital formulary can also be a source of error or delay. The fact that the patient is seen by a pharmacist prior to hospitalization makes it possible to anticipate drug substitutions and possible orders for non-formulary drugs.
Moreover, surgeons do not always have the possibility to prescribe medications taken at home upon admission, which results in a delayed availability of the medication. Thanks to this multidisciplinary project the continuity of treatment is assured.
What was done?
During the preoperative consultation, a pharmacist takes a medication history and enters it into the computerized medical record, making it available for the anaesthetist.
Upon admission of the patient, the continuity of the medication is ensured by the pharmacy.
Indeed, during the admission, the nurse follows a procedure that informs the pharmacy of any medication changes since the preoperative consultation. Afterwards, the pharmacy encodes the treatment into the computerized intra-hospital prescription and delivers it to the department.
Before any drug administration, this treatment is signed by the doctor responsible for the patient.
How was it done?
Preoperative consultations had to be structured so that each patient was first seen by the pharmacist, second by a nurse and third by the anaesthetist.
Thus, the main obstacle was organizational and it was overcome through the centralized management of preoperative clinic appointments.
What has been achieved?
In 2020, 54% of patients admitted for surgery (elective or emergency surgeries) were seen in the preoperative clinic.
What next?
This is an example of good practice as it ensures a standardized medication history and admission management.
THE ROLE OF DNA SEQUENCING AND MOLECULAR TUMOR BOARD COUNSELING IN THE SELECTION OF THE MOST APPROPRIATED THERAPY IN ONCOLOGY
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Marta Anghilieri, Vito Ladisa, Andrea Vingiani, Giancarlo Pruneri
Why was it done?
The new DNA sequencing techniques, globally defined “Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)”, allow parallel sequencing of many samples producing a big amount of data. To give a comprehensive analysis of the data in order to develop new specific and clinically useful therapies, we have introduced the approach to evaluate the data by the MTB, where pharmacists are included as experts of drugs and their preparation and application.
What was done?
The integration of pharmacists into the first Molecular Tumor Board (MTB), a multidisciplinary group, to select the most suitable therapy for oncological patients.
How was it done?
For every patient pharmacists, together with the members of MTB, study the results of NGS to identify known and unknown alterations utilizing a database available to all MTB members. These mutations represent the basic tool to select potential target therapies. The MTB meets weekly to discuss and integrate the alterations observed with the patient clinical history. At the end this approach allows to select the most suitable target therapy.
What has been achieved?
In this study 208 patients affected by No Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) were evaluated. The tumor has an elevated mortality, even if many target drug available or in development, therefore a correct treatment approach is essential to improve the clinical outcome. The NSG identified 117 altered genes. After an extensive literature search, 15 genes were identified as potential target of drugs available. They marked 116 patients potentially tractable with target therapy: 47 patients were candidate to a target therapy already in clinical practice and 69 to a target therapy not in clinical practice. Comparing the two groups, in the candidates to drugs in clinical practice the treatment was started in 65% of cases and in 53% was continued, while in the other group the treatment was started in 23% of cases and in 69% continued.
What next?
• The MTB offers a valid support in the clinical practice
• It individuates a target therapy for a greater number of patients
• The selected therapy has a bigger chance to last longer
• The inclusion of Pharmacist in MTB allow a more aware use and a better selection of drugs
A pharmacist-led pharmacovigilance initiative for the first Austrian Covid-19-vaccination campaign
European Statement
Patient Safety and Quality Assurance
Author(s)
Nikolaus Lindner, Katharina Heitzeneder, Nora Hummer, Elisenda Pichler, Doris Haider
Why was it done?
Due to the lack of long-term safety data, the principal goal was to assure a safe and effective use of the available vaccines by coordinating stringent logistical operating procedures as well as by facilitating early detection and evaluation of possible safety signals. A further objective of this initiative was to increase the awareness among healthcare workers regarding the possible health risks associated with a SARS-CoV-2 infection and Covid-19 vaccines as preventable countermeasures.
What was done?
A Covid-19 vaccination pharmacovigilance campaign was implemented in a clinical setting with the focus on patient safety and quality assurance as part of an employee vaccination rollout. The pharmacy department set up a pharmacovigilance service-point to assess vaccine safety as well as potential adverse events and assure patient care by close follow up.
How was it done?
Assessing and reacting to individual safety signals on time represented a critical challenge. Pharmacists designed questionnaires capturing possible adverse events. In order to lower the barriers for participation it was decided to take a paper-based approach instead of electronic distribution. A pharmacovigilance service-point was continuously managed by two pharmacists directly at the vaccination site to achieve a high response rate. Throughout the campaign the completed questionnaires were simultaneously evaluated, as rapid action was key to detect safety signals early and implement measures accordingly.
What has been achieved?
The results showed a high response rate to the questionnaire of 95% and 53% after the first and second dose, respectively. A significant increase of symptoms after the second dose compared to the first dose reflected the findings of the marketing authorisation study. Based on the analysis no further safety precautions were needed. However, appointments before night or weekend shifts had to be discouraged as well as the vaccination of the whole staff from one department on the same day. As a result, disruptions to patient care could be avoided successfully.
What next?
This initiative serves as a valuable model for upcoming vaccination campaigns and especially for pharmacovigilance projects aiming to assess adverse events of recently approved medicines. Moreover, the successfully implemented multi-disciplinary approach represents the basis for further hospital-wide pharmacy projects and may facilitate the implementation of pharmacist-provided vaccination services.
Clinical impact assessment of pharmaceutical intervention during pharmaceutical consultation of oral therapy-treated cancer patients
Pdf

European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Justine Touchard, Elisabeth Angelier, Isabelle Ferry, Marion Lafay, Jean-Stéphane Giraud, Caroline Giard, Mallory Friou, Laurence Escalup, Thomas Genevée
Why was it done?
For more than 15 years, within the Institut Curie, a pharmaceutical consultation (PC) has been offered to patients undergoing anticancer oral therapy, in addition to a medical announcement consultation and a nurse consultation. The pharmacist secures and optimises drug management through a pharmaceutical analysis of the prescription, an explanation to the patient of drug intake and management of the main side effects.
What was done?
The aim is to assess the Clinical Impact (CI) of Pharmaceutical Interventions (PI).
How was it done?
From 1 January 2020 to 17 March 2020, two types of PI could be collected during each PC. One concerned the prescriber and problems of prescription, while the other concerned patients. Patients could misunderstand some of the information explained by their oncologist. The evaluation of the CI of these PI has been documented by an oncologist based on the Cléo scale v3, validated by a French learned society, Société Française de Pharmacie Clinique. CI of each PI was classified as harmful , null, minor, moderate, major, vital, and not determined.
What has been achieved?
140 PC were carried out. 95% of patients were female and mean age was 62 (±13.73) years. 66 PI were recorded. 39 PI with the prescriber were identified. We noted, among others, 8 risks of possible drug interaction, 9 lacks of prescriptions of support treatment, 3 lacks of drug intake advice and 3 lacks of prescription for blood monitoring.
27 PI with the patient were identified and 21 were relevant. We noted that 7 patients misunderstood drug intake, 5 patients did not know that the previous treatment should have been interrupted, 5 patients misunderstood the monitoring and 4 others were not aware of possible side effects related to their treatment.
The CI was assessed for 83% (n=55) of PI. CI was considered to be minor for 20%, moderate for 53%, major for 14% and vital for 13%. Two prescription errors were associated with vital CI. The first referred to a risk of drug interaction between a proton pump inhibitor and capecitabine. The other error was the risk of loperamide overdosage.
What next?
PC help secure medical care of patients. These results will be presented to our oncologists to improve medical practices.
Impact of a specialist pharmacist on hepato-pancreatico-biliary (HpB) surgical ward rounds at a large tertiary liver centre.
European Statement
Clinical Pharmacy Services
Author(s)
Connor Thompson, Alison Orr
Why was it done?
Surgical patients are at risk of medication-related adverse events, with some of these patients having co-morbidities requiring long-term medications prior to surgery. Published data suggests pharmacist interventions can reduce adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and medication errors and reduce hospital length of stay.
What was done?
The effect of implementing a pharmacist into the HpB surgical ward round (WR) was unknown, this would also support ongoing service development projects in liver pharmacy on patient pathways.
This study aimed to establish the range and clinical impact of interventions made by the specialist pharmacist when attending HpB post-surgical WR as part of ongoing pharmacy engagement and service development.
How was it done?
A prospective study looking at interventions of a specialist pharmacist on WR over a one-month period, attending two WR per week. Review of all post-surgical HpB on an inpatient ward. All interventions collated and categorised based on commonality.
What has been achieved?
Over the course of data collection, the pharmacist reviewed 140 patients and made 477 interventions as part of the WR. This included 45 history medications being started, identification of 32 ADRs to current treatment, 16 instances of vancomycin dose adjustments, confirmation of anticoagulation for 17 patients and addition of 101 antibiotic stop dates contributing to better antimicrobial stewardship. There were also 70 instances of a nurse/doctor/patient requiring additional information on medication treatments.
What next?
This has highlighted the scale of interventions a pharmacist can make on a WR. Emphasising not only adjustment of medications but also the need for medication related information by healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Moving forward a pharmacist will attend at least two WR per week, with potential scope for support in pre-assessment and post-operative clinics to review weaning of analgesia and long-term management of pancreatic replacement for example.
With the recent announcement regarding new standards for the initial education and training of pharmacists in the UK, it would be valuable to assess the impact of a prescribing pharmacist on these WR.

























